“What are AI agents?”… if these new, autonomous AI tools have caught your attention, you’re not alone.
AI agents are all the hype in the world of artificial intelligence, and rightly so. These tools — that can “make decisions and take action” — are changing how companies use AI.
In fact, OpenAI CEO Sam Altman, mentions in his blog:
“We believe that, in 2025, we may see the first AI agents “join the workforce” and materially change the output of companies.”
Keeping up with that vision, many tech giants have developed their own AI agents, which include DeepMind’s Project Mariner, and Nvidia’s Mega. Independent companies, such as Writesonic, too, are making strides in AI agent development.
But, what exactly are these “AI agents” and how can you implement them in your business? If you want to know all about AI agents, this guide is for you. Let’s dive in.
Read In-Depth About AI Agents:
- AI Chatbots vs. AI Agents
- Best AI Agents Examples
- How do AI Agents Work?
- Types of AI Agents
- Benefits of AI Agents
- AI Agent Use Cases and Applications
- AI Agent Best Practices and Ethical Considerations
What are AI agents?
AI agents are artificial intelligence tools that can make and execute decisions on their own, with minimal human input. They use technologies like natural language processing (NLP) as well as external tools to gather data, process it, and take action.
Think of them as employees who never get tired. You initially train or configure them, give the required data, and then they operate independently. But unlike human employees, they don’t need a break and are highly productive.
AI chatbots vs. AI agents
AI chatbots, like ChatGPT, are platforms that use artificial intelligence to provide information, answer questions, and solve customer queries. They work on direct commands and don’t have decision-making capabilities.
AI agents, on the other hand, are programmed to make and execute decisions. They are capable of assessing situations, understanding complex queries, and taking action on their own. Depending on the use case, some AI agents may use AI chatbots or large language models (LLM) as their base technology.
Read our AI agents vs. AI chatbots blog to learn more about their differences.
To understand better, let’s look at some examples of AI agents.
Best AI Agents Examples
- AutoGPT: AutoGPT is an experimental AI agent built on OpenAI’s AI models. It can understand natural language commands, and attempts to complete goals by breaking them into sub-tasks and using available resources like its connected tools and the Internet.
- BabyAGI: It is a simplified version of AGI (Artificial General Intelligence) that understands, creates, and prioritizes tasks independently.
- Project Mariner: It is a web-search AI agent developed by DeepMind that can automate monotonous search tasks through your browser.
- Nvidia Mega: Mega is a blueprint that can help develop, test, and improve physical AI robots for industrial use.
- Chatsonic: An AI marketing agent developed by Writesonic, Chatsonic can automate marketing tasks from research to optimization, including drafting articles and building keyword strategies.
- Agentforce: Developed by Salesforce, Agentforce is a platform that can help you create your own AI agents.
Discover more AI agents to try in 2025 with our list of 12 best AI agents.
Now, if you’ve heard of AI agents, you might’ve also heard of agentic AI. What is that and how’s it different? Let’s find out.
Agentic AI vs. AI agents: What’s the difference?
Agentic AI refers to the broader concept of artificial intelligence systems that can make decisions and take actions autonomously.
AI agents are one such system that can function independently and are a part of the agentic AI concept. They are more task-focused and can only achieve specific goals, making them a subset of agentic AI.
Whereas, agentic AI is the governing ideology that focuses more on the “thinking” or “processing information and taking action” part.
Now that the concept is clear, let’s see how AI agents work.
How do AI Agents Work?
AI agents work in a four-step process: perceive, process, take action, and learn. In a way, it’s quite similar to how we humans perform any task.
Here are the four steps for how AI agents work:
- Perception: It collects data and perceives the situation using sensors if connected to a physical device (smart home devices, self-driving cars) or through previous training if it’s just a digital agent (customer service bots, voice assistants).
- Thought and decision-making: It interprets data, uses problem-solving techniques, checks potential outcomes, uses various algorithms and analyses, and ends up with a decision.
- Action: It executes the decision. This can be adjusting the thermostat, pulling the car to a stop, or conveying information to a customer.
- Learning: It keeps learning from experience, feedback, or new data and gets better as it is used. When faced with similar scenarios, it can make stronger decisions using its new learnings and past experiences.
“A.I. is made by humans, intended to behave by humans and, ultimately, to impact humans lives and human society.” —Fei-Fei Li, CEO of World Labs, at the New Work Summit.
Chatsonic is a great example for an AI agent that’s designed for marketing use cases. Watch this quick Chatsonic demo to get an idea of how an AI agent works.
To perform these steps, AI agents rely on certain key components and reasoning frameworks.
Read our detailed guide on how AI agents work to understand more about their key components and mechanisms.
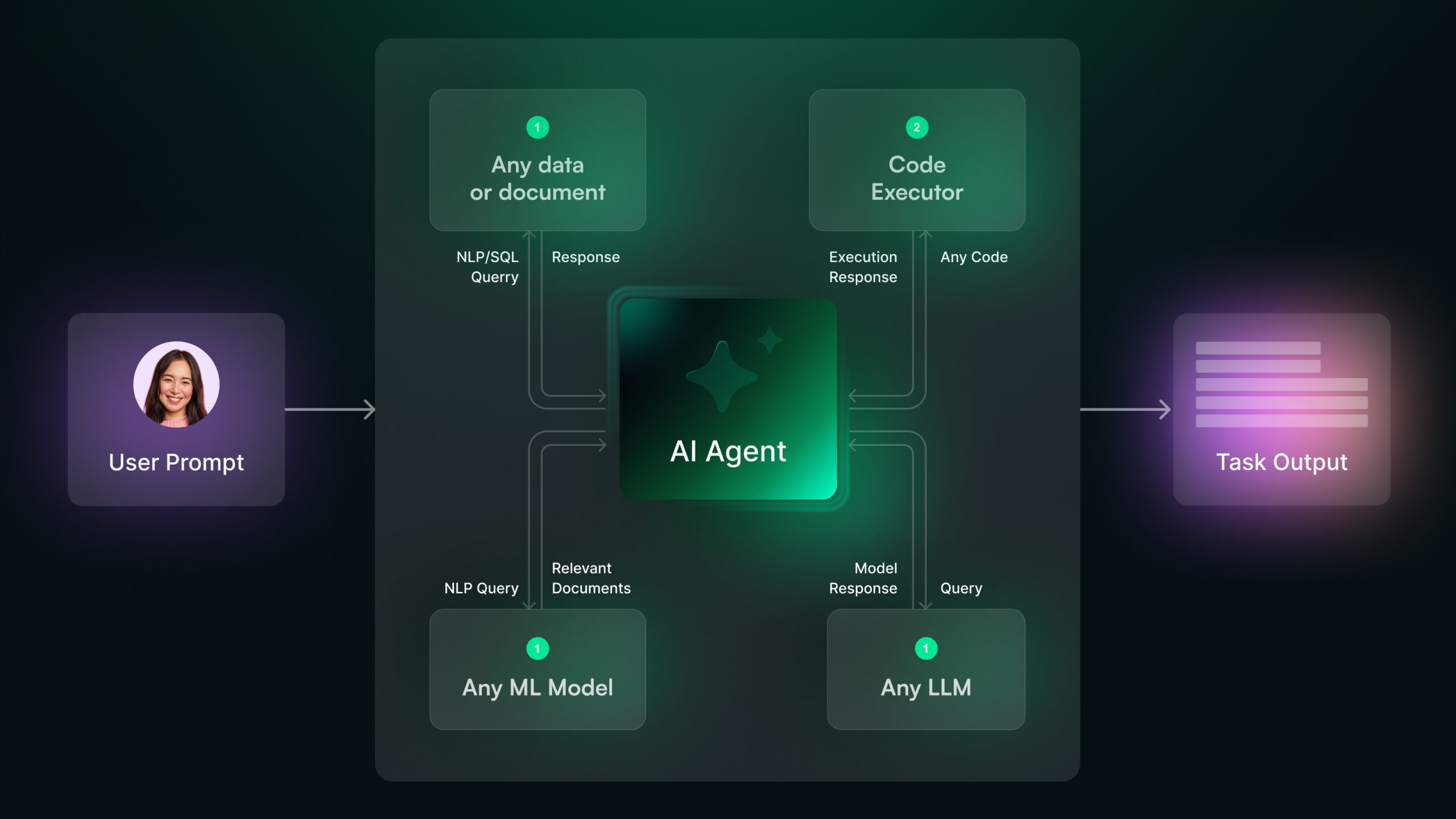
The Key Components of AI Agent Architecture
AI agents rely on several essential components to function effectively. This is called the architecture and is crucial to how they work. Here’s a breakdown of these components:
Large Language Models (LLMs)
Large language models (LLMs) are the components that make AI agents “interactive.” If you’re able to put in queries and understand the solutions given by the agent, that’s thanks to LLMs.
These models, such as OpenAI’s GPT or Google’s Bard, form the foundation of many AI agents. They are trained on massive datasets, which results in better, more human-like output.1
Tools Integration
AI agents often integrate with external tools and APIs to perform tasks. This is what gives them a way to execute actions, which we don’t see in AI chatbots.
For instance, a customer service AI agent might connect to a company’s CRM system to fetch user details, check order statuses, or process refunds. Similarly, a marketing AI agent like Chatsonic could link to SEO tools to conduct keyword research.
Memory systems
Now, if you want to “converse” with AI agents, they need some way to recall information and carry the conversation forward or offer personalized replies. That’s taken care of by their “memory.”
There are basically four types of memories AI agents can hold:
- Short-term memory: Remembers only what is said in a single conversation.
- Long-term memory: Remembers everything from past conversations to the present ones.
- Episodic memory: Remembers certain events and information, but doesn’t recall everything.
- Semantic memory: Only remembers general information available in its database.
When you ask a query or give information, the tools are intelligent enough to assess the importance of the data and then decide which memory to store it in.2
Agent Program
This is the core software that brings together all the components. It governs how the AI agent works, i.e. perceives data, reasons, and acts. Usually, the agent program is designed for specific use cases, such as customer support, marketing, data analysis, and so on.
These form the components of the AI agent’s architecture. However the “brain” of the agent, that is its reasoning, can differ in two ways.
Reasoning Paradigms
Another important aspect of how AI agents work is how they reason and think. These agents employ specific reasoning methods to make decisions and solve problems. The most common ones are ReAct and ReWOO.
ReAct (Reasoning and Action) is a paradigm where the AI agent combines reasoning with actions in real time. It involves analyzing the situation, thinking about the next steps, and acting based on the analysis.3
ReWOO (Reasoning WithOut Observation) is a paradigm where the AI agent thinks of the entire plan upfront. Unlike ReAct, ReWOO agents don’t wait for the outcome of their initial actions to decide on the next one. Instead, they “think” of all possible outcomes, choose the best action course depending on their internal knowledge and previous feedback, and provide an action plan.
These are the key components necessary for AI agents to function. But apart from these, AI agents also follow some key principles.
Key Principles of AI Agents
Understanding the foundational principles of AI agents is essential if you want to use their full potential. These principles govern how AI agents operate, make decisions, and interact with their environment. Let’s explore the key principles that define AI agents:
1. Rational Decision-Making
At their core, AI agents are master decision-makers, carefully weighing options and choosing the most effective path forward. Picture a chess grandmaster who can analyze millions of possible moves in seconds — that’s how AI agents approach problems. They don’t just react; they calculate, predict, and strategize to find the optimal solution.
For instance, when an AI agent manages a smart home system, it doesn’t simply turn lights on and off based on fixed schedules. Instead, it observes patterns in your daily routine, monitors energy usage, and even factors in natural light levels to create the perfect lighting environment while minimizing energy consumption.
2. Perception and Data Analysis
Just as humans use their senses to understand the world around them, AI agents employ sophisticated systems to gather and process information. Their “eyes and ears” come in many forms — from analyzing text and speech to processing sensor data and monitoring network traffic.
Imagine a security AI agent protecting a corporate network. It continuously monitors countless data points: network traffic patterns, user behaviors, system logs, and external threat intelligence. Like an experienced security guard who can spot suspicious activity from subtle cues, the AI agent detects potential threats by recognizing patterns that might escape human notice.
3. Goal-Oriented Behavior
What truly sets AI agents apart is their ability to turn insights into action. They don’t just collect and analyze data – they use this information to make real-world changes. Consider an AI trading agent operating in the stock market. It doesn’t just track market trends; it processes vast amounts of data from multiple sources, including:
- Real-time market prices
- Company financial reports
- Global economic indicators
- Social media sentiment
- News headlines
Based on this analysis, it makes split-second decisions to buy or sell stocks, often performing better than human traders who might be influenced by emotions or fatigue.
While all AI agents operate based on the same principles and components, every AI agent is built for a specific purpose. If you’re planning to use AI agents in your business, it’s important to understand the different types of AI agents and then choose the right one for your requirements.
The 7 Types of AI Agents
These agents are mainly classified depending on how complex their capabilities are. Here are the main types of AI agents you should know about:
Simple reflex agents
These are the simplest forms of AI agents to exist. They work on a fixed set of rules, perform only preprogrammed functions and use already available information from their database.
These types of agents can’t be trained and they also don’t have any conversation memory. That means you can’t give follow-up commands or queries.
Example: Automatic door sensors. If they detect motion, they open the door. If not, the door remains closed.
Model-Based Reflex Agents
These agents go a step further by having a basic understanding of how the world works. They can predict how their actions will affect the environment and make better decisions.
They have limited short memory but still are bound by a set of rules.4
Example: A GPS-based map that adjusts the route to show the fastest one, based on how much traffic is on each route.
Goal-Based Agents
These agents don’t just react—they aim to achieve specific goals. They think ahead and plan the best steps to reach their objective.
Example: A self-driving car calculates how to safely navigate traffic to reach its destination.
Utility-Based Agents
These agents are a step ahead of the goal-based ones. Utility-based agents aim to not just reach a goal but to do it in the best possible way. They evaluate different options and pick the one that gives the most benefit or satisfaction.
Example: The same self-driving car. But now, it chooses the best speed for optimal fuel efficiency, along with navigating traffic.
Learning Agents
These agents learn and improve over time. Even though they have preprogrammed rules, they get better by observing, trying, and learning from their experiences. They also have conversation memory to replicate results during future interactions.
Example: Generative AI agents become better at answering questions the more they interact with people.
Hierarchical Agents
Hierarchical agents represent a more complex and structured approach. These agents are organized in multiple levels, with higher-level agents managing the tasks of lower-level agents. They perform similar tasks and aren’t independent.
Example: An AI manufacturing agent in an automotive plant. The lower-level agents handle smaller manufacturing tasks while the higher-level agents oversee the manufacturing process as a whole.
Multi-Agent Systems (MAS)
Sometimes, multiple agents work together to achieve a common goal. These are complex systems that “communicate” and “collaborate” with each other to complete the task at hand.5
Example: A smart home system where lights, thermostats, and security cameras work together to make your home comfortable and safe.
Read our detailed guide to learn more about the types of AI agents.
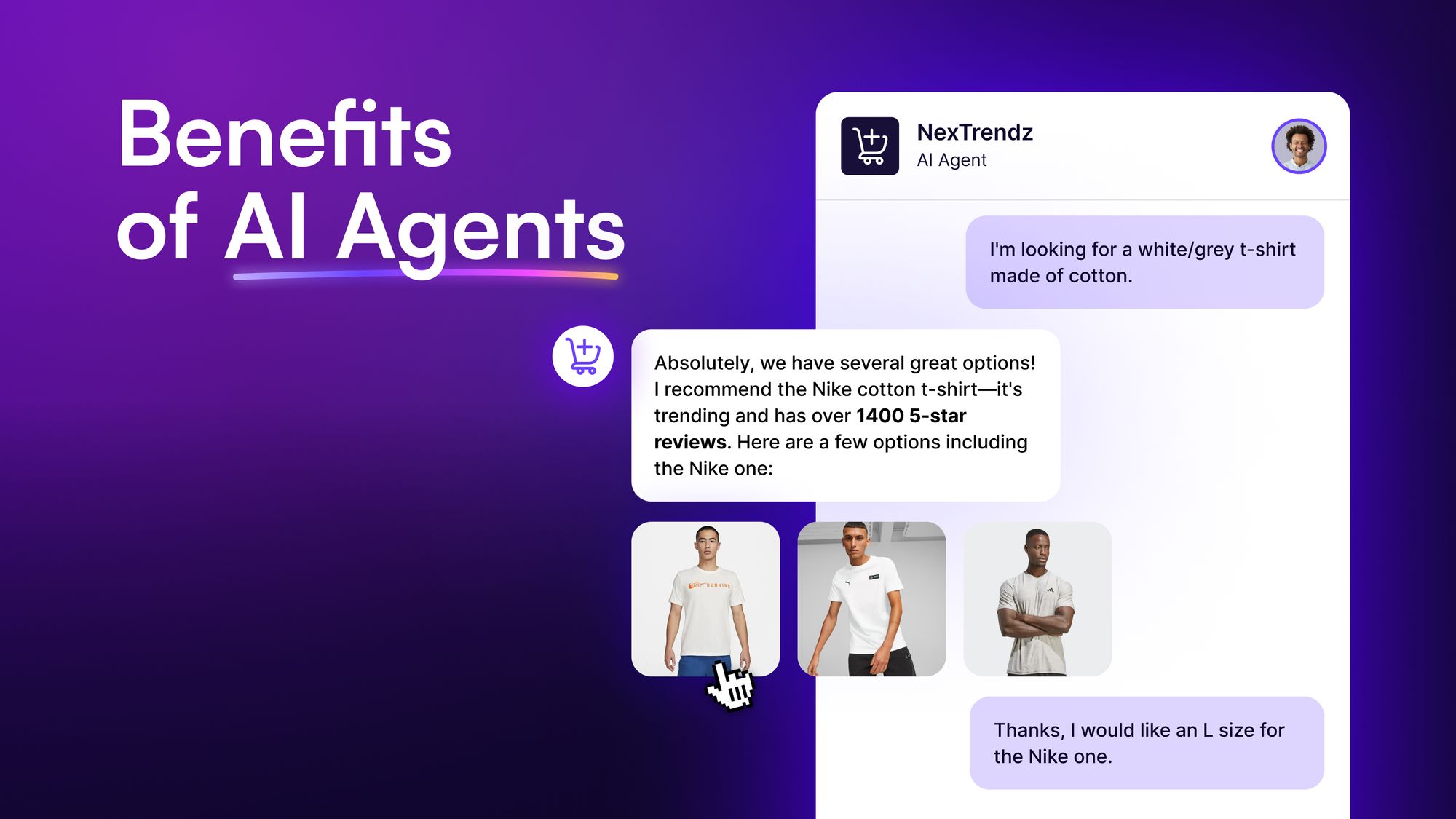
Benefits of Using AI Agents for Your Business
Think of an AI agent as your “ideal” teammate. It can handle manual tasks plus it’s highly productive, always concentrates on the task at hand, and is available all the time. Sounds superhuman? It’s quite like that.
Here’s a full list of how AI agents can benefit you:
Improves productivity and efficiency
If you’ve understood AI agents, you know that they’re capable of continuously handling tasks. But that’s not the only way they make your team efficient.
AI agents also don’t need manual intervention, most of the time. That means, your human teammates can focus on tasks that actually need their attention, while the AI agent handles the monotonous ones.
Enhanced customer experience
AI agents make interactions feel personal by understanding what each customer likes and needs.6 They’re always available—day or night—to answer questions and offer tailored recommendations, which can boost customer engagement and loyalty.
They’re also proactive, spotting potential problems before they happen and fixing them to keep things running smoothly.
Consistency
One of the best things about AI agents? They don’t mess up or forget. Your customers will always get accurate, reliable results, no matter how many times they ask questions.
Scalability
Running a new product launch or an end-of-the-year sale? Regardless of how high the support question volumes are, you can prepare to accommodate them with AI agents. They are highly scalable and can process multiple queries at once, depending on the bot’s bandwidth.
And since AI agents already process basic queries and tasks, there are fewer queries for your human agents to handle.
Cost-Effectiveness
By automating routine tasks and processes, AI agents can help reduce operational costs. They require minimal human intervention, which means you can allocate your workforce to more strategic and productive activities.
Wondering why you should use AI agents? Learn more about the benefits of AI agents for your business.
Due to these benefits, businesses have been implementing AI agents into various processes. Check out some of these real-life use cases of AI agents.
Applications of AI Agents in Real Life
“You can build a very rich agentic world defined by this tapestry of AI agents that can act on our behalf across our work in life, across teams, business processes, as well as organizations.” —Satya Nadella at Microsoft Ignite, 2024.
AI agents can be used in any business process where data analysis, problem-solving, and human input are required. A single AI agent can handle all these steps, and also implement the final action plan, creating a seamless and efficient workflow.
Here are some common AI agent use cases in businesses:
Customer Support AI Agents
AI agents handle customer queries, provide troubleshooting steps, and even process refunds or order replacements without human intervention.
Example: A SaaS company support AI agent may diagnose issues with the software on the customer’s end and provide troubleshooting solutions.
E-commerce AI Agents
These AI agents analyze user behavior and create personalized campaigns for e-commerce businesses.
Example: An e-commerce AI agent can send customized discounts based on a user’s browsing history and purchase patterns.
Healthcare AI Agents
AI agents in healthcare assist in patient care by monitoring health data and alerting doctors about abnormalities.
Example: A wearable AI agent in fitness bands can track heart rates and notify users or healthcare providers if it detects irregularities.
Smart Home AI Agents
These AI agents manage connected devices, ensuring optimal energy usage and convenience.
Example: A smart home AI agent can adjust the thermostat based on your schedule or turn off lights if there’s no one in the room.
Supply Chain Management AI agents
Supply chain management AI agents optimize inventory levels and predict demand trends.
Example: An AI agent for a retailer might forecast which products will sell most during the holiday season and make sure they have sufficient inventory.
Content Marketing AI Agents
Content marketing AI agents suggest keywords, create content strategies, and write content that’s optimized for search engines.
Example: Marketing AI agents can help with SEO keyword research and content planning.
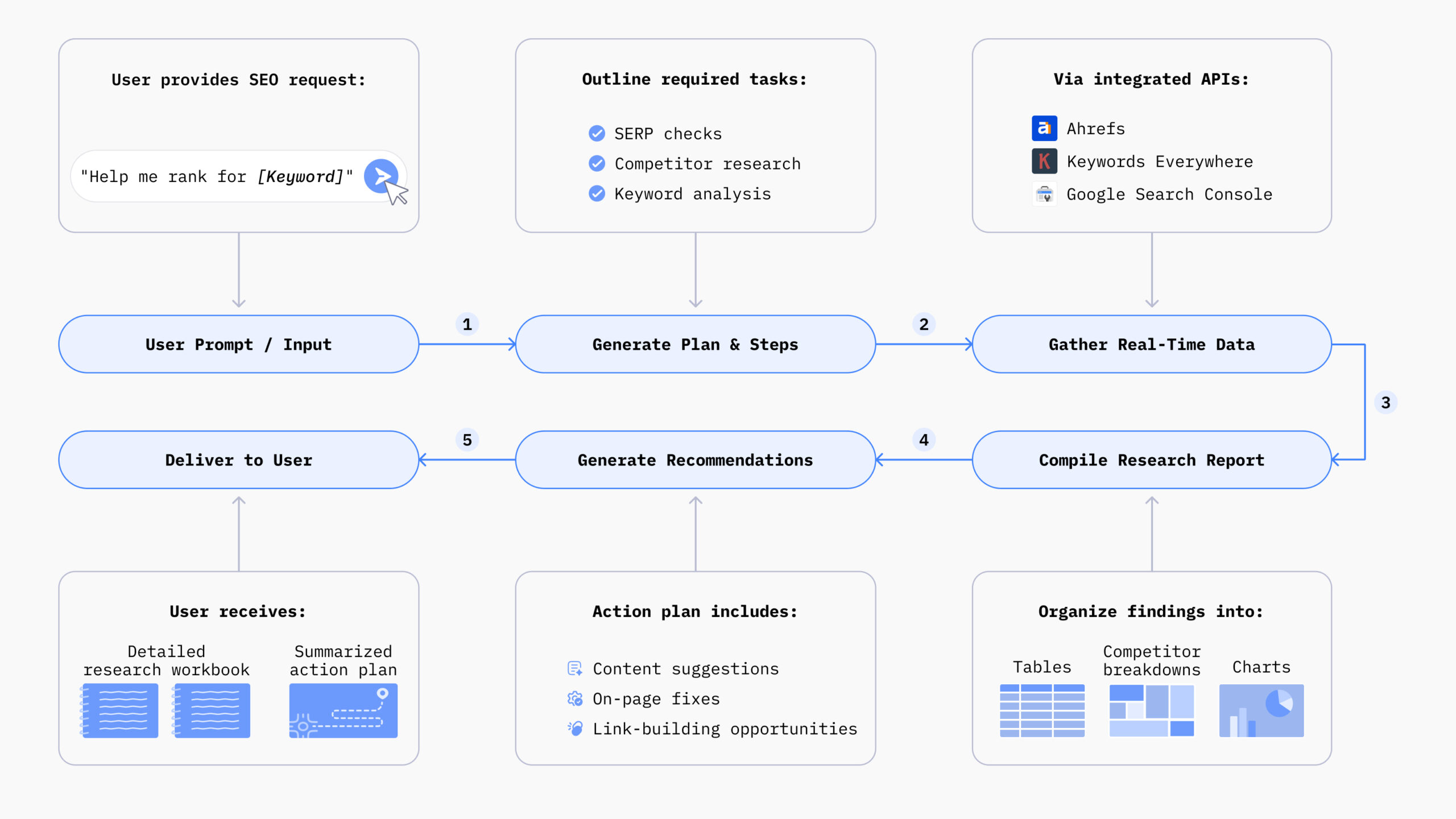
Chatsonic, a marketing AI agent by Writesonic, is one such tool that can assist you with content marketing.
Want to discover more AI agent applications? Check out our article to find 20+ AI agent use cases for your business.
To understand how AI agents can benefit your business and how you can use them, let’s look at a popular example: Amazon Web Services or AWS.
The Power of AWS in AI Agent Development
Amazon Web Services has created a powerful ecosystem where AI agents can thrive. Think of AWS as a fully equipped laboratory where scientists can conduct groundbreaking experiments. Here’s how AWS empowers AI agent development:
Amazon SageMaker: The AI Workshop
SageMaker serves as your complete AI development studio, providing everything needed to build and train AI agents. It’s like having a high-tech workshop where you can:
- Design and test AI models using pre-built components
- Access powerful computing resources for training
- Deploy agents seamlessly across different environments
Amazon Connect Contact Lens: The Customer Service Revolution
This sophisticated system transforms customer service operations by:
- Analyzing customer conversations in real-time
- Identifying customer sentiment and emotions
- Automatically categorizing and prioritizing issues
- Generating detailed insights for service improvement
Now that you’re familiar with what AI agents are and how they work, let’s see how you can actually implement them in your business processes.
Implementing AI Agents in Your Organization
Successfully implementing AI agents requires careful planning and a strong foundation. The success of AI agent implementation in any organization depends on two critical elements: clear objectives and quality data. Let’s explore how to establish these essential components for your organization’s AI journey.
Setting the Stage: Defining Clear Objectives
Implementing AI agents is like constructing a sophisticated building – success begins with a detailed blueprint that guides every step of the journey. Rather than settling for vague aspirations like “improve efficiency,” organizations need to craft specific, measurable targets that illuminate the path to transformation.
Picture a bustling customer service department embracing AI transformation. Their objectives tell a compelling story of evolution:
- Transform customer response times from a lengthy 30 minutes to a brisk 5 minutes, ensuring customers spend time finding solutions rather than waiting in queues
- Boost first-contact resolution rates by 40%, meaning customers walk away satisfied from their very first interaction
- Maintain customer satisfaction scores above 90%, creating a consistent experience that keeps customers coming back
- Enable AI agents to handle 70% of routine inquiries independently, allowing human agents to focus their expertise on complex cases that require nuanced understanding
The Foundation: Data Preparation and Management
Think of data as the vital fuel that powers your AI agents’ performance. Like a professional athlete who carefully selects and prepares their nutrition for peak performance, AI agents require meticulously curated data to operate at their full potential.
Creating a Robust Data Diet
Your AI system must effortlessly blend diverse data streams while maintaining pristine accuracy. Consider a retail AI agent, which weaves together:
- Point-of-sale transactions that reveal the rhythms of customer purchasing
- Customer browsing patterns that illuminate the path from interest to purchase
- Real-time inventory levels that pulse with the ebb and flow of stock
- Seasonal trends that map the changing tides of consumer demand
- Competitor pricing data that paints a picture of the market landscape
Data Hygiene and Organization
Imagine your data as a modern digital library where every piece of information has its designated place, readily accessible when needed. This meticulous organization demands:
- Removing duplicate entries to maintain a single source of truth
- Standardizing data formats to ensure seamless communication
- Creating logical categories that make information retrieval intuitive
- Establishing clear relationships between data points to reveal deeper insights
This thoughtfully structured approach ensures your AI agents can navigate the data landscape efficiently, making informed decisions based on a foundation of clean, well-organized information that flows naturally through your systems.
However, implementing AI agents comes with its own challenges and limitations. You need to be aware of these beforehand to tackle them effectively and ensure your AI agent-based processes run smoothly.
Challenges and Limitations of Using AI Agents
By now, you know what AI agents are, how they work, and their applications. And while AI agents offer numerous benefits, it is also good to be aware of the challenges and limitations that you may face when implementing them:
Ethical Concerns and Bias
AI agents can inadvertently perpetuate biases present in their training data. This can lead to unfair or discriminatory outcomes, especially in sensitive areas like hiring or loan approvals. Usually, it is quite necessary but difficult to ensure unbiased and fair responses in topics related to Your Money or Your Life (YMYL) when using AI agents.
Data Privacy and Security
AI agents often require access to large amounts of data to function effectively. This raises concerns about data privacy and security, especially when handling sensitive customer information. Businesses must ensure robust data protection measures and comply with privacy regulations like GDPR.
Lack of Contextual Understanding
Despite advancements, AI agents can still struggle with nuanced context and complex scenarios. This limitation can lead to misinterpretations or inappropriate responses, particularly in customer-facing roles.
Dependence on Quality Data
The effectiveness of AI agents heavily relies on the quality and quantity of data they’re trained on. Obtaining high-quality, diverse, and unbiased data sets can be challenging and expensive.
Lack of Emotional Intelligence
AI agents, while efficient, often lack the emotional intelligence and empathy that human employees possess. This can be a limitation in roles that require a high degree of emotional understanding or complex interpersonal skills.
Best Practices and Ethical Considerations of AI Agents
As AI agents grow in capabilities and adoption, their ethical use and proper implementation have become critical. Below, we discuss key considerations and best practices to ensure responsible AI deployment:
1. Addressing Bias and Fairness
AI agents can inadvertently perpetuate biases present in their training data, leading to unfair outcomes. For example, recruitment AI agents may favor certain demographics if trained on biased hiring data. In fact, one of Amaqzon’s AI recruiting agents was found to be biased against women.
Even though AI in itself doesn’t have “emotions” and “judgments,” it’s not capable of bias on its own. However, it is trained with human data. And when even subtle biases are present in that data, AI agents tend to amplify it.
To minimize these, conduct regular audits of training datasets and outcomes to identify and mitigate biases. Ensure diverse, high-quality data during development and implement new technologies like retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) to keep AI agents fair.
2. Ensuring Data Privacy and Security
AI agents often process sensitive user information, making them susceptible to privacy breaches. Mishandling data can lead to legal and reputational risks.
To ensure data protection and privacy, implement robust data encryption, comply with regulations like GDPR or CCPA, and adopt practices like anonymizing data to safeguard user privacy.
3. Enhancing Transparency and Accountability
If you’re using AI agents, it’s important to let your employees, customers, users, or any other stakeholders know about AI usage. Users must understand how AI agents make decisions, especially in critical areas like finance or healthcare. A lack of transparency can reduce trust and impact customer relationships.
You can build transparency by providing clear documentation of how you use AI and how it makes decisions. Also, if you’re using customer data to train the AI agents, it’s crucial to specify that, too.
4. Managing Dependency and Failures
Over-reliance on AI agents without proper oversight can lead to operational disruptions if the system fails or makes errors.
To avoid this, establish fallback mechanisms and keep human oversight as a safety net for high-stakes tasks. Continuously test and update AI agents to improve reliability.
5. Promoting Ethical Usage Across Applications
AI agents can be misused by anyone. Say an employee has access to an AI agent, they can use it for automating harmful activities or creating manipulative content. Responsible implementation is crucial to prevent such outcomes.
It’s also essential that you develop ethical guidelines for your AI applications. Additonally, regularly review use cases to ensure they align with societal and organizational values.
Learn more about AI agent best practices and ethical considerations through our detailed guide.
How AI Marketing Agent Chatsonic Can Help
Chatsonic is one of the best marketing AI agents that you can choose for your business. From writing content to conducting keyword research and conducting competitive analysis, using the AI agent is like having a marketing expert at your fingertips.
The AI agent relies on multiple LLMs and has well-known SEO and content-writing tools integrated into its workflow. With one single, conversational command, you can build and execute entire content strategies for your website — all within a few minutes.
Want to build an efficient marketing strategy with AI agents? Try Chatsonic today!
FAQs on What are AI Agents
1. Why are AI agents important?
AI agents automate repetitive tasks, enhance efficiency, and solve complex problems, all with minimum human input. They are quite useful in industries like healthcare (diagnosing diseases), education (personalized learning), and transportation (autonomous driving). By reducing human effort and improving decision-making, AI agents allow humans to focus on tasks that actually demand their attention.
2. Is ChatGPT an AI agent?
No, ChatGPT is not an AI agent. Rather, it is an AI chatbot. While ChatGPT has diverse capabilities which include searching the web and answering queries, it requires “prompts” or “human commands” to carry out any task. It is not capable of independent decision-making, which is the defining factor of an AI agent.
3. Is Alexa an AI agent?
No, Alexa is not yet an AI agent. Though it has some AI capabilities such as voice recognition, it cannot perform tasks independently. However, Amazon does plan to deploy Alexa as an AI agent by rehauling its foundation model and including new AI technologies.
4. What are the 7 types of AI agents?
The 7 types of AI agents are simple reflex agents, model-based reflex agents, goal-based agents, utility-based agents, learning agents, hierarchical agents, and multi-agent systems (MAS).
5. What is an AI agent in real-life examples?
An AI agent in real-life example is Chatsonic, an AI marketing agent that’s used by marketers to create content, research keywords, optimize articles, and publish them on various platforms. Another example is Project Mariner, an AI agent by DeepMind that automates web browsing tasks.
References
- Brown, T. B., Mann, B., Ryder, N., Subbiah, M., Kaplan, J., Dhariwal, P. & Amodei, D. (2020). “Language models are few-shot learners” ↩︎
- Kim, T., Cochez, M., François-Lavet, V., Neerincx, M., & Vossen, P. (2023). “A Machine with Short-Term, Episodic, and Semantic Memory Systems”
↩︎ - Shunyu Yao, Student Researcher, and Yuan Cao, Research Scientist, Google Research, Brain Team. “ReAct: Synergizing Reasoning and Acting in Language Models” ↩︎
- Stone, P., & Veloso, M. (2000). “Multiagent systems: A survey from a machine learning perspective” ↩︎
- Schmid, S., Schraudner, D., & Harth, A. (2021). “Performance comparison of simple reflex agents using stigmergy with model-based agents in self-organizing transportation” ↩︎
- Mohannad A. M. Abu Daqar, Ahmad K. A. Smoudy (2019). “The Role of Artificial Intelligence on Enhancing Customer Experience” ↩︎






![What is Grok 3? A Detailed Guide to the AI Model [+Examples]](/wp-content/uploads/7.1-2.png)

































![How to Scale Your Business Using B2B AI Agents [+ Tools to Try]](/wp-content/uploads/B2B-AI-Agents-scaled.jpg)



![40 AI Agent Use Cases Across Industries [+Real World Examples]](/wp-content/uploads/AI-Agent-Use-Cases-1-scaled.jpg)