Remember the last time you gave a command to an AI chatbot? You type something, and it responds. That’s impressive but also limiting.
But autonomous AI agents work differently.
They don’t wait for your commands. Instead, they make decisions independently, learn from what works (and what doesn’t), and take action without constant human input.
In fact, you’re probably using these agents daily without knowing it.
So, if you want to understand how these agents work and what they can do for your business, keep reading to learn about:
- What is autonomous AI, and how does it differ from traditional agentic AI.
- Autonomous AI agents examples across real-world applications.
- Different types of autonomous AI agents
- What the future holds for an autonomous agent in AI.
What is an autonomous AI agent, and how do they work?
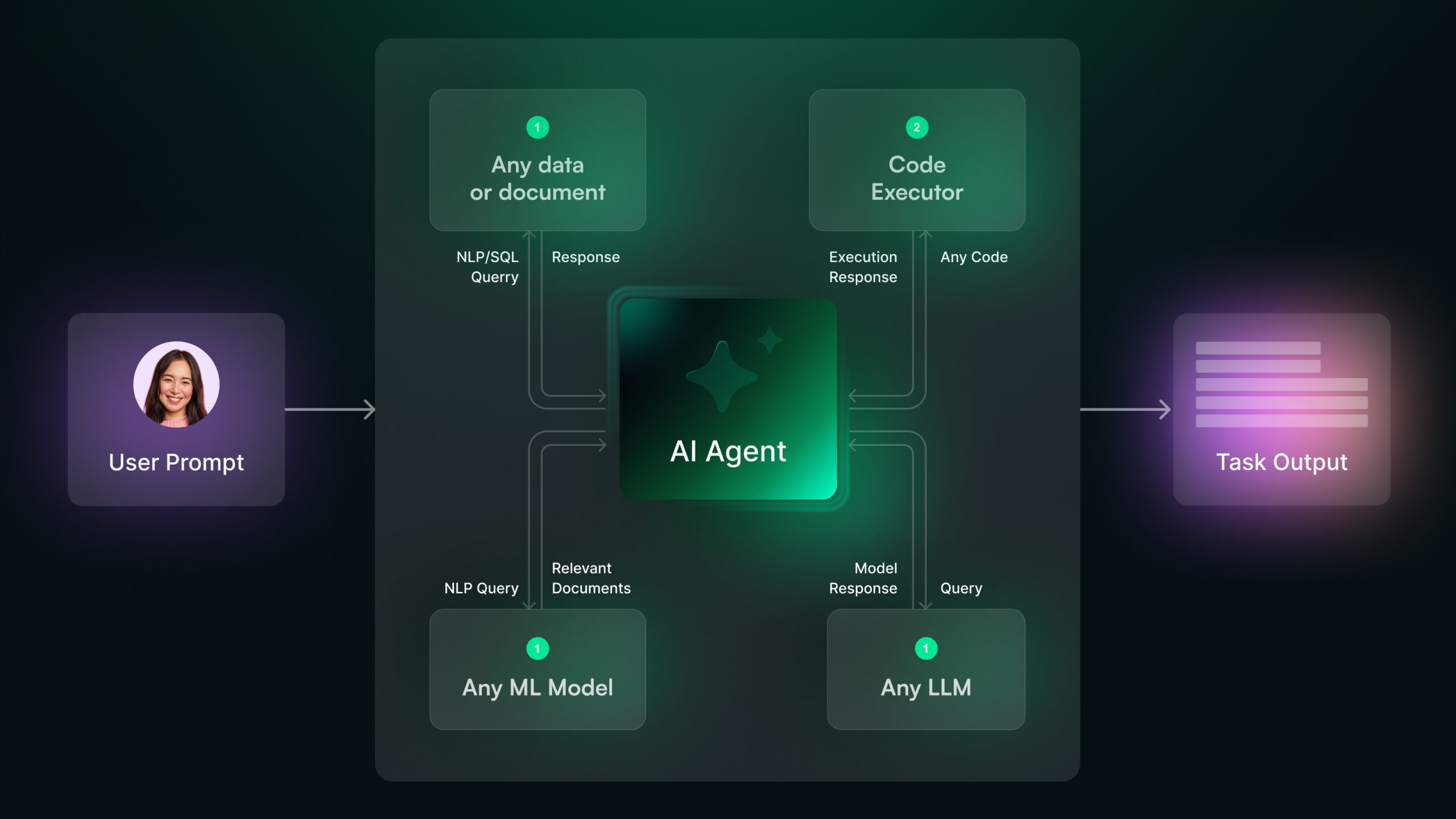
An autonomous AI agent combines multiple capabilities that make them truly powerful. They don’t just collect and analyze information. These agents act on their knowledge and learn from the results.
That’s what makes them different from traditional AI chatbots that simply respond to commands.
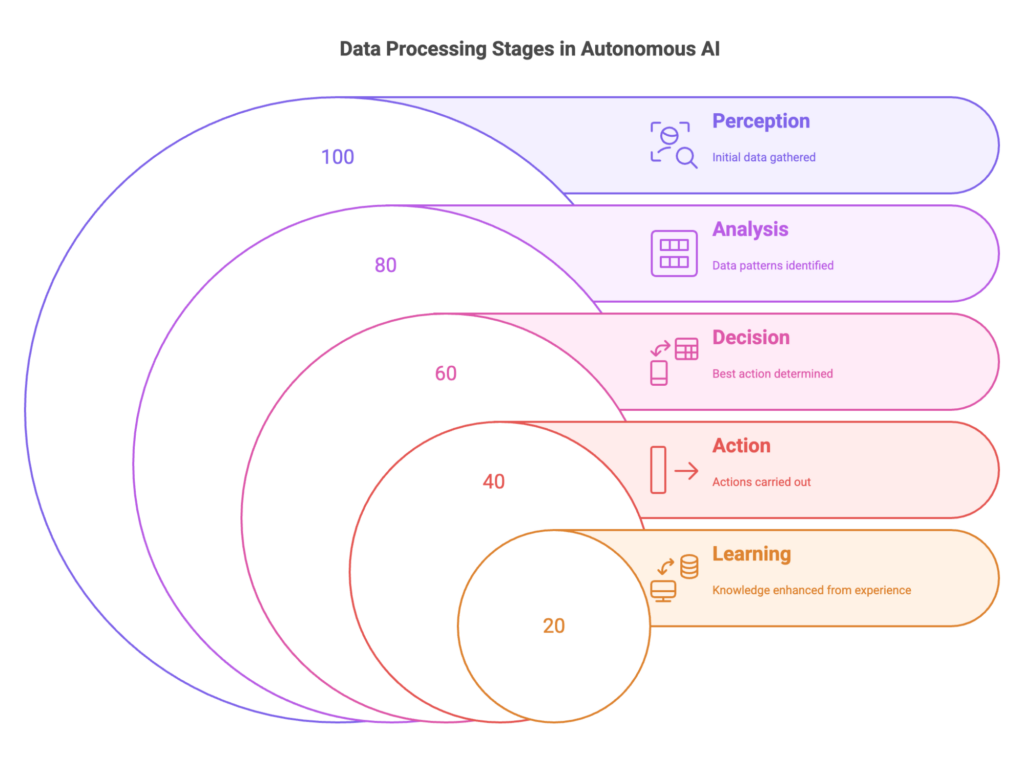
Here’s a five-step process of how autonomous agents work:
- Perception: It collects data from multiple sources like databases, sensors, and external tools.
- Analysis: The agent processes this data using machine learning to spot patterns.
- Decision: Based on the analysis, it chooses the best action.
- Action: It executes the chosen steps independently.
- Learning: The agent updates its knowledge from each experience.
The magic happens when AI agents tap into Large Language Models (LLMs) and connect with external tools. They can browse websites, check databases, and use APIs to get real-time data. That means you get accurate, contextual responses every time.
More importantly, these agents don’t stay static — they keep getting better.
After each task, the agentic AI updates its knowledge and fine-tunes its decision-making process. Soon enough, they handle complex tasks that seemed impossible before.
As a result, autonomous AI agents can adapt quickly to new situations. When circumstances change, they adjust their approach automatically. That makes them perfect for tasks where flexibility matters.
Your AI agent can even team up with other agents and systems. They share information and work together on complex problems, creating better solutions than they could alone.
How autonomous agents differ from traditional AI
Traditional AI, or non-agentic AI, typically operates within predefined parameters and requires continuous human input to function effectively.
These systems are designed to perform specific tasks or answer queries based on their training data and algorithms.
In short, autonomous agents highlight a key differentiator: the ability to operate with minimal human intervention.
To further understand the unique aspects of autonomous agents, let’s look at the core characteristics behind how AI agents work:
- Independence: Autonomous agents can perform complex tasks without constant human oversight.
- Adaptability: They can change their approach based on the environment and new information.
- Learning capability: Autonomous agents use machine learning to improve over time.
- Complex task management: They can break down and manage complicated jobs into smaller, manageable steps.
These characteristics set autonomous agents apart from regular AI tools, which often lack the same level of independence and adaptability.
💡Learn more about: Differences between AI Agents vs. AI Chatbots
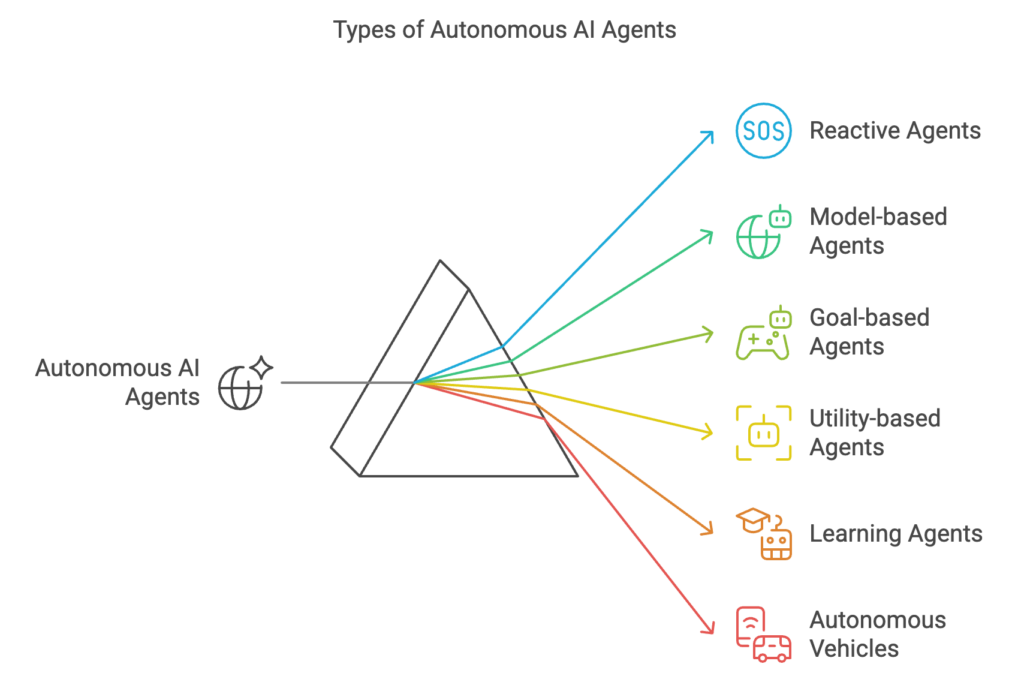
7 types of autonomous AI agents
1. Reactive agents
Reactive agents represent the simplest form of autonomous AI, operating based solely on current perceptions without maintaining an internal state or considering past experiences.
These agents are designed to respond immediately to stimuli in their environment, making them exceptionally fast in their decision-making process.
While they can be relied upon to produce the same output for a given input consistently, this also means they lack the ability to learn or improve over time.
Despite their simplicity, reactive agents can be highly effective in controlled environments where quick, consistent responses are crucial.
Example: Reactive agents are extensively used in creating opponents for games like chess, where the AI responds to the current board state without considering previous moves.
Another significant application is in basic robotic systems, particularly in manufacturing settings, where robots need to react quickly to their environment, such as avoiding obstacles or responding to changes on an assembly line.
2. Model-based agents
Model-based agents represent a significant step up in complexity from reactive agents, as they maintain an internal representation or model of their environment.
This internal model allows the agent to consider how the world evolves independently of its own actions and how its actions will affect the world.
By leveraging this model, these agents can predict potential future states, enabling more informed and sophisticated decision-making processes.
Their ability to simulate different scenarios internally gives model-based agents a distinct advantage in handling complex, dynamic environments where the consequences of actions may not be immediately apparent.
Example: One of the most prominent applications of model-based agents is in weather prediction systems, where complex models of atmospheric conditions are used to forecast future weather patterns.
In the automotive industry, autonomous vehicles rely heavily on model-based agents to navigate roads safely, continuously updating their internal model of traffic conditions, road layouts, and potential hazards.
3. Goal-based agents
Goal-based agents introduce a new level of autonomy by incorporating specific objectives into their decision-making process. These agents evaluate different courses of action based on how well they satisfy predefined goals, allowing for more flexible and purposeful behavior.
Unlike simpler agents that merely react to their environment, goal-based agents can create and execute complex plans to achieve their objectives.
This goal-oriented approach enables them to adapt to new situations by formulating appropriate strategies, even if they haven’t encountered the exact scenario before.
Example: GPS systems exemplify goal-based agents, planning routes to reach specified destinations while considering factors like traffic, road conditions, and user preferences.
In logistics and supply chain management, these agents optimize warehouse operations and delivery routes, constantly adjusting plans to meet delivery deadlines while minimizing costs.
4. Utility-based agents
These agents assign utility values to various possible states or outcomes, allowing them to make nuanced decisions that balance multiple, often conflicting, objectives.
The ability of these agents to handle multi-faceted decision-making scenarios makes them invaluable in any field where complex trade-offs need to be made systematically.
Example: In the financial sector, utility-based agents are extensively used in algorithmic trading systems, making investment decisions by balancing potential returns against risks.
Recommender systems in e-commerce and streaming platforms often employ utility-based agents to suggest products or content, considering factors like user preferences, item popularity, and platform goals.
Whereas in healthcare, these agents assist in treatment planning by weighing the potential benefits of different medical interventions against their risks and costs.
💡Also read: 40 AI Agent Use Cases Across Industries [+Real World Examples]
5. Learning agents
Learning agents represent the cutting edge of autonomous AI, characterized by their ability to improve performance over time through experience.
These agents employ various machine learning techniques, such as reinforcement learning, supervised learning, or unsupervised learning, to adapt their behavior based on feedback from their environment.
By analyzing historical data and outcomes, learning agents can refine their decision-making processes, discover new strategies, and even adapt to changing environments or goals.
Example: Personal digital assistants like Siri or Alexa exemplify learning agents, continuously improving their responses and capabilities based on user interactions.
Autonomous vehicles are also a great example of learning agents that can refine their driving skills, adapting to different road conditions, traffic patterns, and driving cultures.
6. Autonomous vehicles
While not a traditional AI agent category, autonomous vehicles represent a significant and highly visible application of autonomous AI technology.
These systems integrate multiple types of AI agents, combining reactive elements for immediate response to road conditions, model-based components for navigation and traffic prediction, goal-based planning for route determination, and learning capabilities for continuous improvement.
Autonomous vehicles rely on complex sensors, including cameras, LIDAR, and radar, to perceive their environment in real-time. They process this information using sophisticated AI algorithms to make split-second steering, acceleration, and braking decisions.
7. Autonomous robots
Autonomous robots represent another significant category in the field of autonomous AI, characterized by their ability to perform physical tasks in the real world with minimal human intervention.
These robots combine various AI agent types to perceive their environment, make decisions, and execute actions.
They often employ sophisticated sensor arrays and computer vision systems to understand their surroundings, coupled with advanced control systems for precise movement and manipulation.
Example: Amazon uses robot fleets for inventory management and order fulfillment. Autonomous robots are being developed for applications like surgery assistance, patient care, and hospital logistics.
Exploration robots, designed to operate in environments too dangerous or inaccessible for humans, are used in deep-sea research, space exploration, and disaster response scenarios.
💡Check out: 12 Best AI Agents You Need to Try in 2025
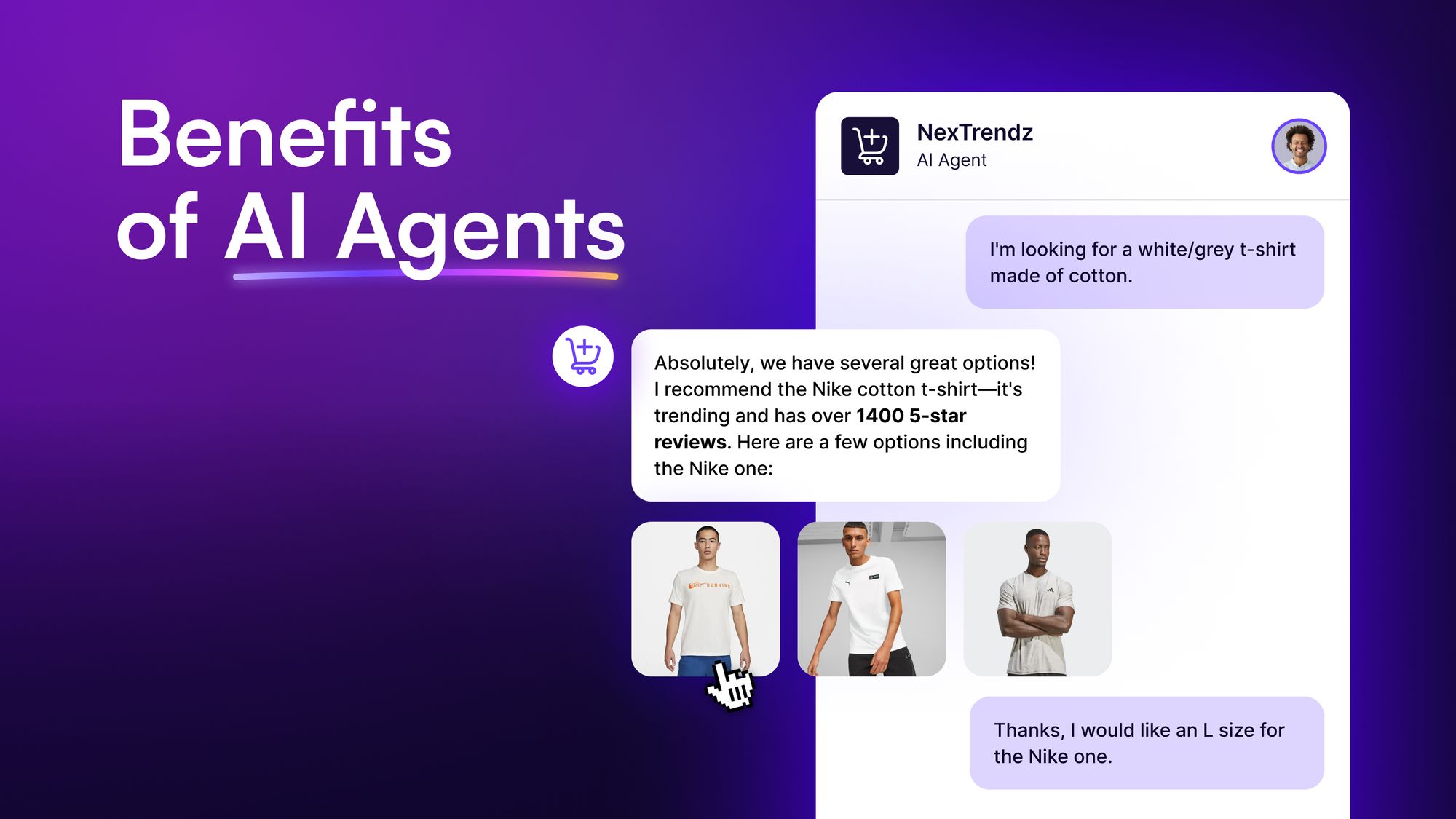
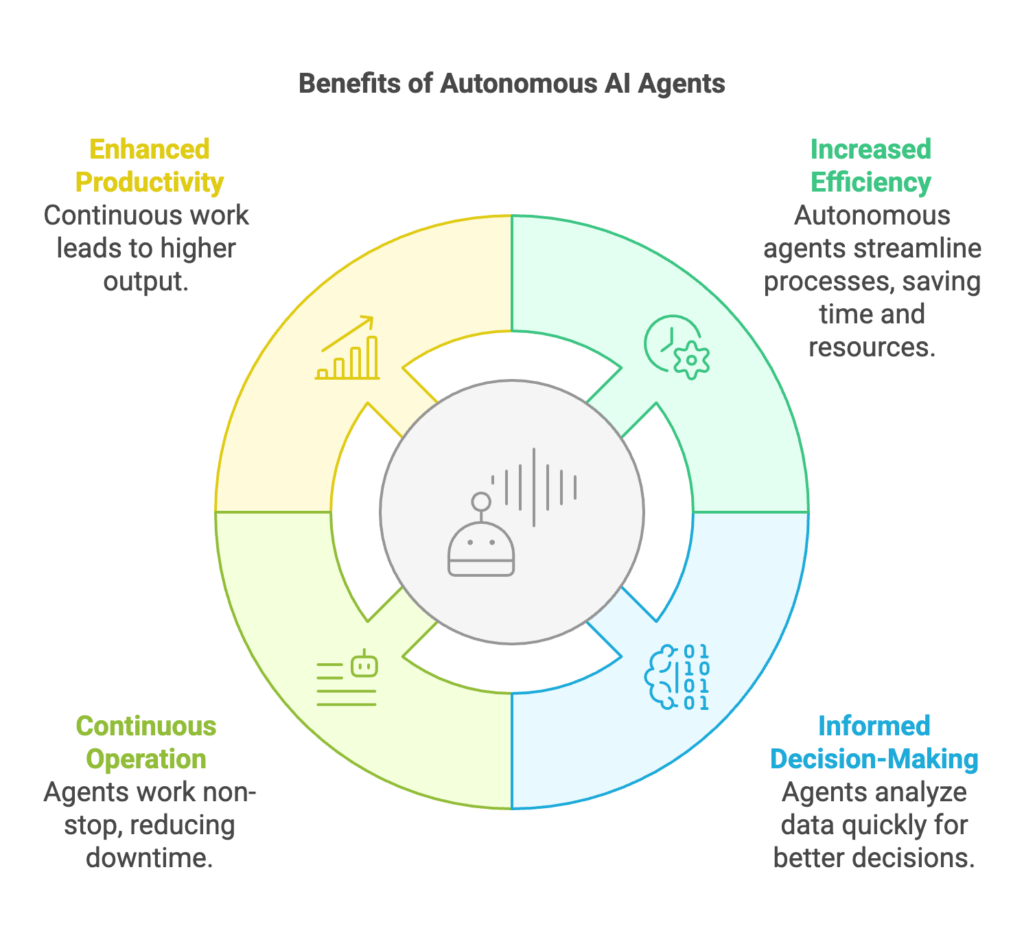
Benefits of an autonomous AI agent
1. Enhanced efficiency and productivity
AI agents excel at automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks, allowing humans to focus on more complex, creative, and strategic activities. These agents can work tirelessly 24/7 without fatigue, significantly increasing overall productivity.
For instance, in customer service, AI chatbots can handle multiple inquiries simultaneously, reducing wait times and freeing up human agents to deal with more complex issues.
In manufacturing, AI-powered robots can perform precise and repetitive tasks with consistent quality, leading to higher production rates and reduced errors.
2. Improved decision making
AI agents can process and analyze vast amounts of data at speeds far beyond human capabilities. This ability enables them to identify patterns, trends, and insights that might be overlooked by human analysts.
AI agents can analyze market trends, economic indicators, and company performance data in fields like finance to make more informed investment decisions.
Whereas in healthcare, autonomous AI agents can assist doctors by analyzing patient data, medical literature, and treatment outcomes to suggest personalized treatment plans, potentially leading to better patient outcomes.
3. Enhanced accuracy and reliability
AI agents are not subject to human limitations such as fatigue, emotional bias, or lapses in concentration, which can lead to errors.
As a result, for tasks requiring high precision and consistency, AI agents can maintain a level of accuracy that is difficult for humans to match over extended periods.
This is particularly valuable in fields like quality control in manufacturing, where AI-powered visual inspection systems can detect defects with remarkable accuracy. In financial services, AI agents can process transactions and perform audits with high precision, reducing the risk of errors and fraud.
4. Cost reduction
While the initial investment in AI technology can be significant, the long-term cost savings can be substantial. AI agents can perform tasks more quickly and efficiently than human workers, reducing labor costs.
They can operate 24/7 without additional compensation, sick leave, or benefits. In industries like customer service, AI chatbots can handle a large volume of basic inquiries, reducing the need for large customer support teams.
5. Scalability and flexibility
AI agents offer unparalleled scalability, handling increasing workloads without a proportional resource increase. This scalability is particularly valuable in digital services, where AI agents can manage sudden spikes in user activity without degradation in performance.
Additionally, AI agents can be quickly reprogrammed or retrained to adapt to new tasks or changing business needs, offering a level of flexibility that is hard to achieve with human workforces.
This adaptability is crucial in fast-paced industries where market conditions and customer preferences can change rapidly.
6. Personalization and enhanced user experience
AI agents excel at processing individual user data to provide highly personalized experiences.
For example, AI systems in e-commerce can analyze a user’s browsing and purchase history to suggest products they are likely to be interested in, enhancing the shopping experience and increasing sales.
They can also curate personalized playlists or viewing recommendations in content streaming services, increasing user engagement and satisfaction.
This level of personalization extends to various sectors, from personalized learning in education to tailored financial advice in banking.
7. 24/7 availability and instant response
Unlike human workers, AI agents can provide round-the-clock service without breaks. This continuous availability is particularly valuable in global businesses operating across different time zones.
For example, in customer support, AI chatbots can respond instantly to queries anytime, improving customer satisfaction and reducing response times.
In IT operations, AI agents can monitor systems continuously, detecting and responding to real-time issues and minimizing downtime and potential losses.
💡For more information: Top 7 Benefits of AI Agents With Examples and Use Cases
Real-world autonomous AI agents examples
1. Virtual assistants: Siri, Alexa, Google Assistant
Virtual assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant are AI-powered software agents designed to help users with various tasks through voice commands or text input. These assistants can:
- Set reminders and alarms
- Answer questions by searching the internet
- Control smart home devices
- Make phone calls and send messages
- Provide weather updates and traffic information
- Play music and podcasts
- Offer personalized recommendations based on user preferences
For example, you can say, “Hey Siri, remind me to buy milk tomorrow at 10 AM,” and the assistant will create a reminder.
Or you can ask, “Alexa, what’s the weather like today?” and receive a forecast before heading outside.
These assistants use natural language processing to understand user queries and machine learning to improve their responses over time. They can also integrate with various apps and services to expand their capabilities.
Virtual assistants have become an integral part of our daily lives, offering voice-activated support for various tasks.
These AI-powered assistants are continuously evolving, becoming more conversational and context-aware.
2. Autonomous vehicles: Tesla
Tesla remains at the forefront of autonomous vehicle technology, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in self-driving cars. However, the journey to full autonomy is ongoing and faces several challenges.
Tesla’s Full Self-Driving (FSD) technology continues to advance, but it has not yet achieved the unsupervised autonomy predicted by Elon Musk.
Crowdsourced data has revealed discrepancies between Tesla’s claims and real-world performance, indicating that truly autonomous driving may still be years away.
Safety concerns and regulatory hurdles remain significant obstacles to adopting autonomous vehicles.
While full self-driving is still in development, current Tesla vehicles with autopilot can:
- Maintain lane position and adjust speed in traffic
- Change lanes automatically when the driver activates the turn signal
- Navigate on-ramps and off-ramps on highways
- Recognize and respond to traffic lights and stop signs
- Park themselves in parallel or perpendicular spaces
For instance, a Tesla using autopilot on a highway can maintain a safe distance from the car in front, adjust its speed according to traffic flow, and even suggest and execute lane changes for optimal routing.
The AI system uses data from multiple cameras, radar, and ultrasonic sensors to create a 360-degree view of the car’s surroundings.
3. Autonomous agents in marketing
Autonomous AI agents in marketing are designed to optimize various aspects of digital marketing strategies.
These agents can analyze customer data, optimize campaigns, and automate many marketing tasks. A prime example of an advanced AI marketing agent is Chatsonic.
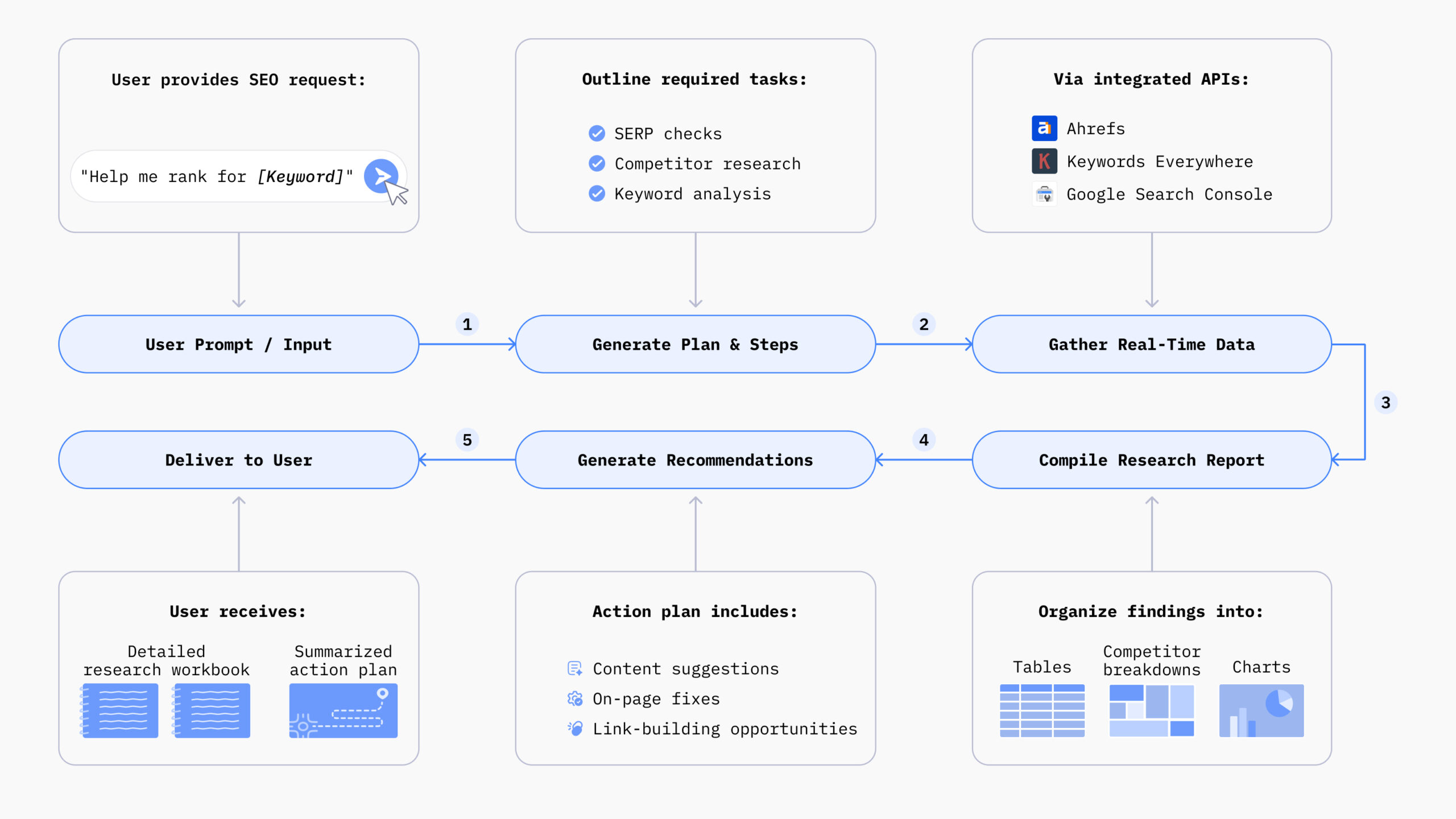
Chatsonic is an all-in-one AI marketing agent that can handle a wide range of marketing tasks, including:
- Content creation: Chatsonic can generate high-quality articles, blog posts, and social media content. It uses advanced natural language processing to create engaging, SEO-optimized content that aligns with your brand voice.
- Keyword research and SEO optimization: With integrations to tools like Ahrefs, Chatsonic can perform in-depth keyword research and provide SEO recommendations. It can conduct keyword research and competitor analysis and suggest ways to optimize content for better search engine rankings.
- Content strategy development: The AI agent can analyze market trends, competitor content, and audience preferences to help develop comprehensive content strategies. It can identify content gaps and suggest topic clusters to improve your website’s topical authority.
- Performance analysis and reporting: By integrating with key marketing tools like Google Search Console, Chatsonic can provide insights into performance and suggest data-driven improvements.
- Personalization: The AI agent can analyze customer data to create personalized marketing messages and product recommendations, enhancing the customer experience and potentially increasing conversion rates.
For example, a marketer can use Chatsonic to research keywords for a new ad campaign, generate topic clusters for blogs, create social media content to promote the posts, and then analyze performance – all within a single platform.
What sets Chatsonic apart from generic AI chatbots is its deep integration with marketing-specific tools and data sources.
This intuitive agent doesn’t just generate content but does so with a strategic marketing perspective, considering SEO, content creation, and industry best practices based on real-time web search.
4. Smart home devices
The smart home market is experiencing rapid growth, driven by AI integration and increasing consumer demand for connected devices. These autonomous agents transform our living spaces into more efficient and responsive environments.
In fact, according to a Statista report, the global smart home user base is projected to reach 424.5 million by 2028, highlighting the widespread adoption of these technologies.
Smart home devices powered by autonomous AI can automate and optimize various aspects of home management, such as:
- Adjust heating and cooling systems based on occupancy and learned preferences.
- Control lighting based on natural light levels and user habits.
- Manage home security systems, including smart locks and cameras.
- Optimize energy usage by turning off unused devices and suggesting energy-saving measures.
- Automate grocery ordering by tracking consumption and predicting when items need to be restocked.
For instance, a smart thermostat like Google’s Nest can learn a household’s routines and automatically adjust the temperature to save energy when no one is home.
It can also be controlled remotely via a smartphone app, allowing users to adjust settings from anywhere.
5. NPCs in video games
Artificial Intelligence is revolutionizing non-player characters (NPCs) in video games, making them more realistic, adaptive, and engaging. This advancement is creating more immersive and dynamic gaming experiences.
AI-driven NPCs are becoming increasingly human-like, with the ability to form relationships, take consistent actions, and react in nuanced ways to player choices.
Plus, with memory systems, these non-player characters can remember past encounters and adjust their behavior accordingly, creating a more personalized gaming experience.
NPC-to-NPC interactions create dynamic social ecosystems within games, leading to evolving relationships and social structures.
The integration of AI in video games is expected to create “infinite replay value” and unique, tailored experiences for each player.
A survey revealed that 79% of gamers would be more likely to buy a game with AI NPCs, and 81% would be willing to pay more for such games.
💡You might also like: Top AI Agent Trends for 2025
The future of autonomous AI agents
According to CMSWire, the AI agents market size was valued at USD 3.7 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 103.6 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 44.9% over the period 2024-2032.
As these agents continue to grow and evolve, let’s take a look at what you can expect from them in the near future:
1. Emotional intelligence augmentation
By 2027, AI agents will present better emotional intelligence by becoming smarter, more ethical, and better at understanding emotions, leading to more efficient, personalized services.
This means future autonomous agents in AI will be able to recognize and respond to subtle emotional cues in text, voice, and even facial expressions.
These “EQ Boosters” will analyze subtle facial expressions, voice tonality, and physiological signals in real time, providing users with profound insights into others’ emotional states and suggesting nuanced responses.
Here are a few emotionally intelligent autonomous AI agent examples we can expect to see in the future:
- Dispute mediation for corporate settings by objectively analyzing communication patterns and suggesting innovative compromises that human mediators might overlook.
- Recruiters can incorporate these agents into interviewing processes to identify emotional cues presented by candidates.
- Customer experience will be more personalized by AI voice generation detecting emotional cues.
2. Quantum-enhanced AI agents
Integrating quantum computing with AI agents by 2028 will usher in an era of problem-solving capabilities that defy classical limitations.
Here are some industries that can benefit from quantum computing integrations with AI:
In climate modeling, quantum AI agents will process complex climate data for more accurate predictions and counterintuitive solutions for climate change mitigation.
We can also expect to see the drug discovery process to transform as these agents use quantum simulations to speed up finding new drugs and design molecules with properties once thought impossible.
3. Autonomous creative collaborators
In the film industry, AI directors will take the lead in creating movies, making real-time decisions on lighting, camera angles, and even guiding actor performances.
These AI directors will introduce new narrative structures and visual styles that break traditional cinematic rules, resulting in entirely new film genres.
In fact, Open AI’s Sora is already making waves for its realistic and high-quality AI video generation output.
The art world will witness the emergence of “Evolutionary Art,” where AI agents create “living” digital artworks that evolve based on viewer interactions, global events, and even the collective emotional state of its audience.
These pieces will challenge our understanding of authorship and the very definition of art itself.
💡Also check out: 14 Best AI Image Generators to Boost Your Visuals in 2025
4. Ethical dilemma navigators
As AI becomes more integrated into decision-making processes, a new class of AI agents will emerge to navigate ethics and best practices for artificial intelligence in businesses.
AI ethicists will be embedded in corporate and governmental decision-making systems, ensuring that automated processes align with evolving societal values and ethical standards.
These agents will follow predetermined rules and engage in real-time philosophical reasoning to address novel ethical challenges.
We can also expect to see the emergence of “Moral Uncertainty Resolvers,” which will tackle scenarios with conflicting ethical frameworks by modeling various philosophical approaches and suggesting the most ethically robust course of action.
This could lead to the development of new ethical theories that bridge cultural and ideological divides.
Autonomous AI agents are no longer a concept of the future—they are a present-day reality reshaping industries, businesses, and our daily lives.
Their ability to operate independently, adapt to new situations, and continually learn makes them a transformative force in areas ranging from healthcare and finance to marketing and creative arts.
As these agents evolve, their potential will only grow.
From enhancing human emotional intelligence and tackling global challenges with quantum precision to redefining creativity and ethics, autonomous AI agents are set to lead humanity into an era of unprecedented innovation and collaboration.
Whether you’re an entrepreneur seeking to leverage its capabilities or a curious mind exploring the cutting edge of technology, now is the time to dive in and embrace autonomous AI.
The future is autonomous, adaptive, and agentic.
Are you ready to join it?





































![How to Scale Your Business Using B2B AI Agents [+ Tools to Try]](/wp-content/uploads/B2B-AI-Agents-scaled.jpg)



![40 AI Agent Use Cases Across Industries [+Real World Examples]](/wp-content/uploads/AI-Agent-Use-Cases-1-scaled.jpg)