Artificial intelligence is evolving beyond simple automation. Two of the most transformative systems today are agentic AI vs generative AI, but both serve entirely different purposes.
Generative AI is about content creation—generating text, images, videos, or code based on learned patterns.
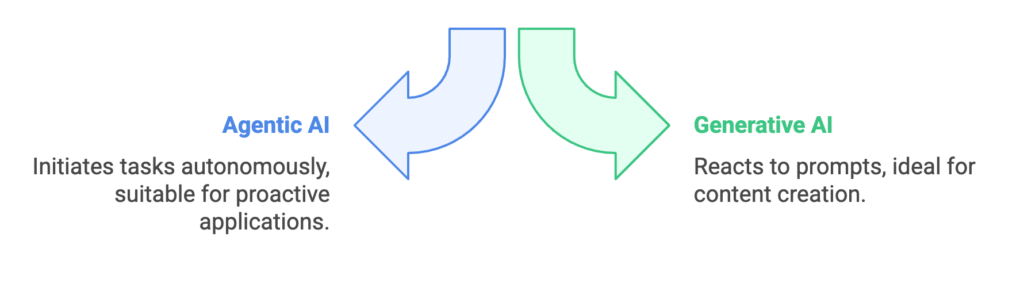
Meanwhile, agentic AI is about action—it makes decisions, executes multi-step tasks, and operates autonomously. Unlike generative AI, it doesn’t just generate content; it plans and takes action without constant human guidance.
So, how do these two AI systems differ in functionality, decision-making, learning mechanisms, and real-world applications? More importantly, which one is best suited for your business or industry?
This guide breaks down agentic AI vs. generative AI, its strengths and limitations, and how they can work together to enhance workflows.
What is agentic AI?
Agentic AI is a smart system that can make and execute decisions independently, with minimal human input.
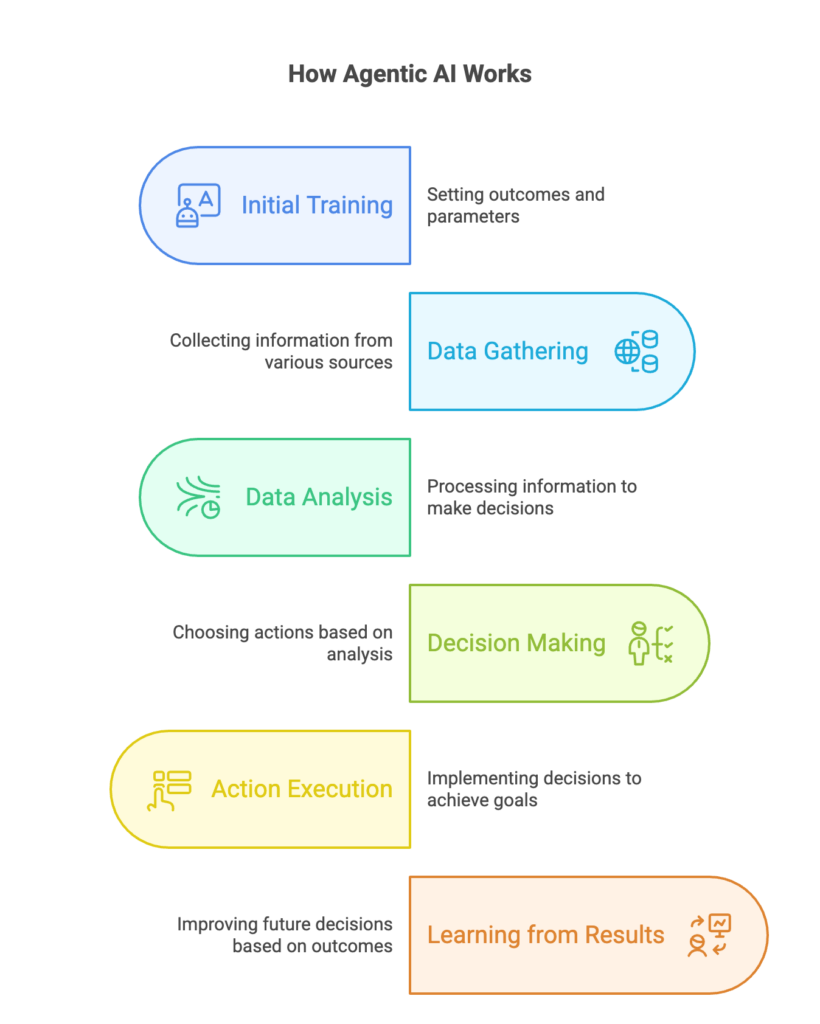
You initially train it and set different outcomes. But, once configured, it works as an autonomous AI agent, analyzing situations, making decisions, and taking actions to achieve goals.
The way agentic AI works is similar to how humans make decisions.
Just like we gather information, process it, take action, and learn from experience, agentic AI follows four key steps:
- Gathers data from various sources.
- Analyzes the information to make decisions.
- Takes specific actions based on analysis.
- Learns from results to improve future decisions.
Agentic AI’s ability to connect with other tools and platforms makes it powerful, pulling in data and insights to make better decisions. Here are some of the benefits and use cases of agentic AI:
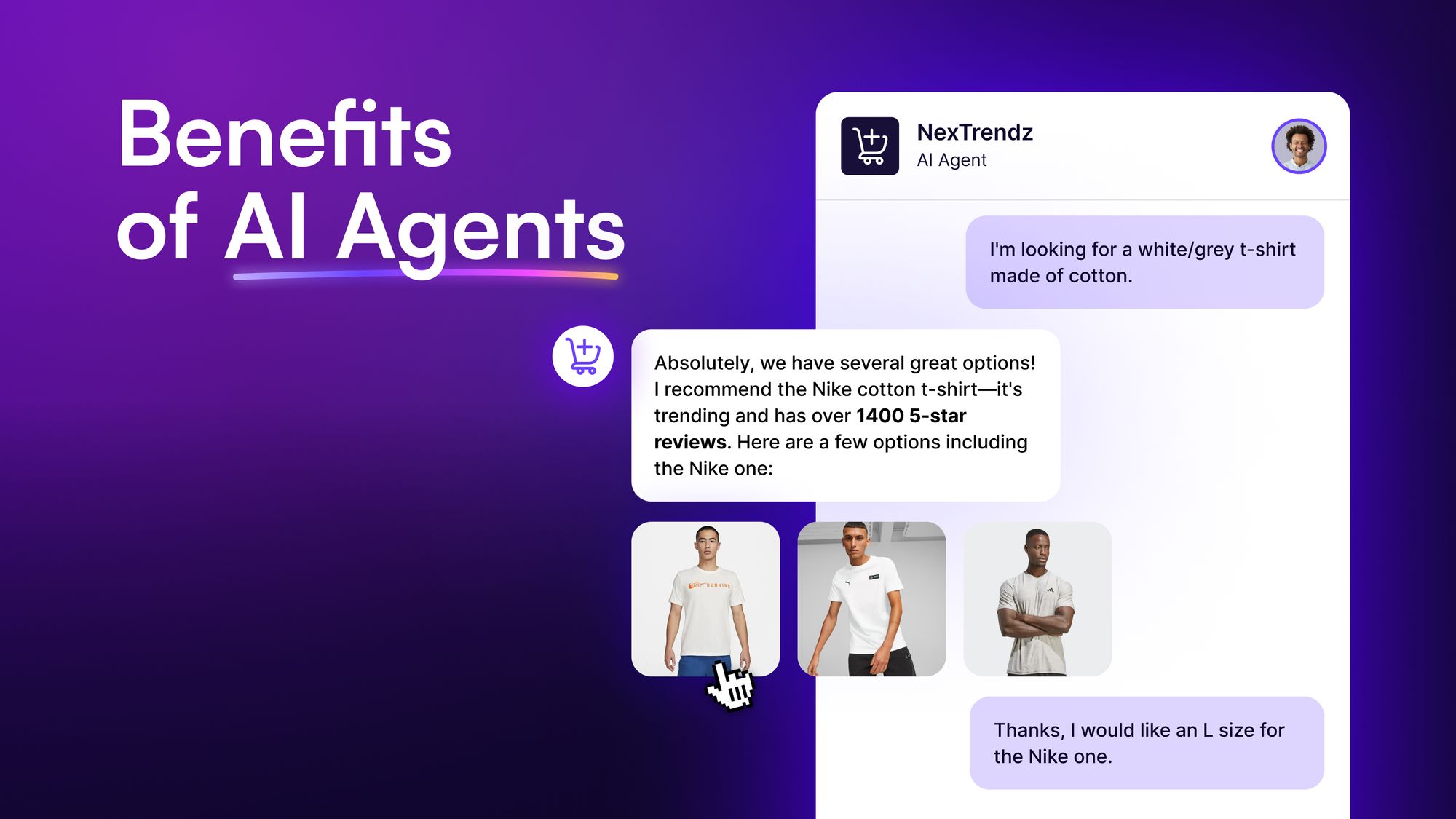
1. Automating complex workflows
AI agents can handle multi-step tasks without human oversight. For example, a customer support agent can analyze a ticket, find a solution, and respond without human input.
2. AI-assisted research and decision-making
AI-driven business intelligence agents can gather market data, compare competitor strategies, and generate reports automatically.
3. Personal AI assistants
AI agents like OpenAI’s Operator can plan daily schedules, summarize meetings, schedule tasks, or even automate email responses.
4. AI for engineering and coding
Developers use AI coding agents to automate debugging, refactor code, and suggest optimizations.
5. AI for smart operations
Supply chain AI agents predict inventory needs, optimize delivery routes, and prevent delays.
Companies see real results with agentic AI. Industry analysis shows AI agents could automate up to 30% of work hours by 2030. Customer service has improved substantially, too. Over half of service professionals report better customer interactions, faster response times, and happier customers.
💡 Learn more about: Types of AI Agents to Streamline Your Workflow
What is generative AI?
Generative AI (GenAI) is artificial intelligence that creates new content, such as text, images, videos, or code. Unlike agentic AI, which focuses on autonomy and task execution, generative AI tools specialize in producing human-like outputs based on patterns learned from data.
At its core, generative AI doesn’t just retrieve or predict—it generates original content.
The economic footprint of generative AI grows faster every day. Research shows this technology could add between USD 2.60 trillion to USD 4.40 trillion annually to businesses of all sizes.
Key features of generative AI include:
- Content creation: Can generate text, images, music, or even videos from prompts.
- Data training: Learns from vast datasets to mimic human creativity.
- Context understanding: Processes language and context to produce coherent, relevant content.
- Customizability: Adapts outputs based on user preferences and styles.
- Multi-modal capabilities: Can generate text-to-image, text-to-video, or even text-to-code outputs.
Research shows that 75% of generative AI’s value potential focuses on four key areas:
- Customer operations
- Marketing and sales
- Software engineering
- Research and development
Generative AI works by first training on massive datasets, such as text, images, or audio, to understand patterns and relationships.
Models like GPT-4 for text or DALL·E for images analyze this data to recognize how elements fit together. The AI predicts and generates the most relevant output based on learned patterns when given a prompt.
Over time, some models refine their responses using user feedback or additional prompts, improving accuracy and relevance.
💡 You might also like: AI Agents vs. AI Chatbots: What Is The Difference?
Agentic AI vs generative AI: A detailed comparison
Gen AI and agentic AI are two distinct but complementary branches of artificial intelligence.
While generative AI focuses on creating new content, agentic AI is designed to think, plan, and act independently.
This fundamental difference shapes how they function, learn, make decisions, and integrate into various systems.
Understanding their strengths and limitations is crucial for businesses, developers, and AI enthusiasts looking to leverage these systems for automation, creativity, or decision-making.
| Aspect | Agentic AI | Generative AI |
| Primary Purpose | Acts as autonomous decision-maker; task execution-oriented | Functions as content creator; output-driven |
| Follows prompts, no autonomous thinking; predicts the best answer based on training data | Continuous learning and adapts through reinforcement learning and memory systems | Predictive pattern recognition based on massive datasets |
| Decision-making Process | Goal-oriented and autonomous; can execute complex multi-step plans | Follows prompts, no autonomous thinking; predicts best output based on training data |
| System Integration | Multi-system integration; can connect with various tools and software for workflow automation | Typically standalone or API-based; limited inherent interaction with external systems |
| Operational Mode | Proactive and self-sufficient; anticipates needs and takes action independently | Reactive and prompt-driven; only works when given specific instructions |
1. Functionality and primary purpose
Agentic AI: Function as autonomous decision-makers:
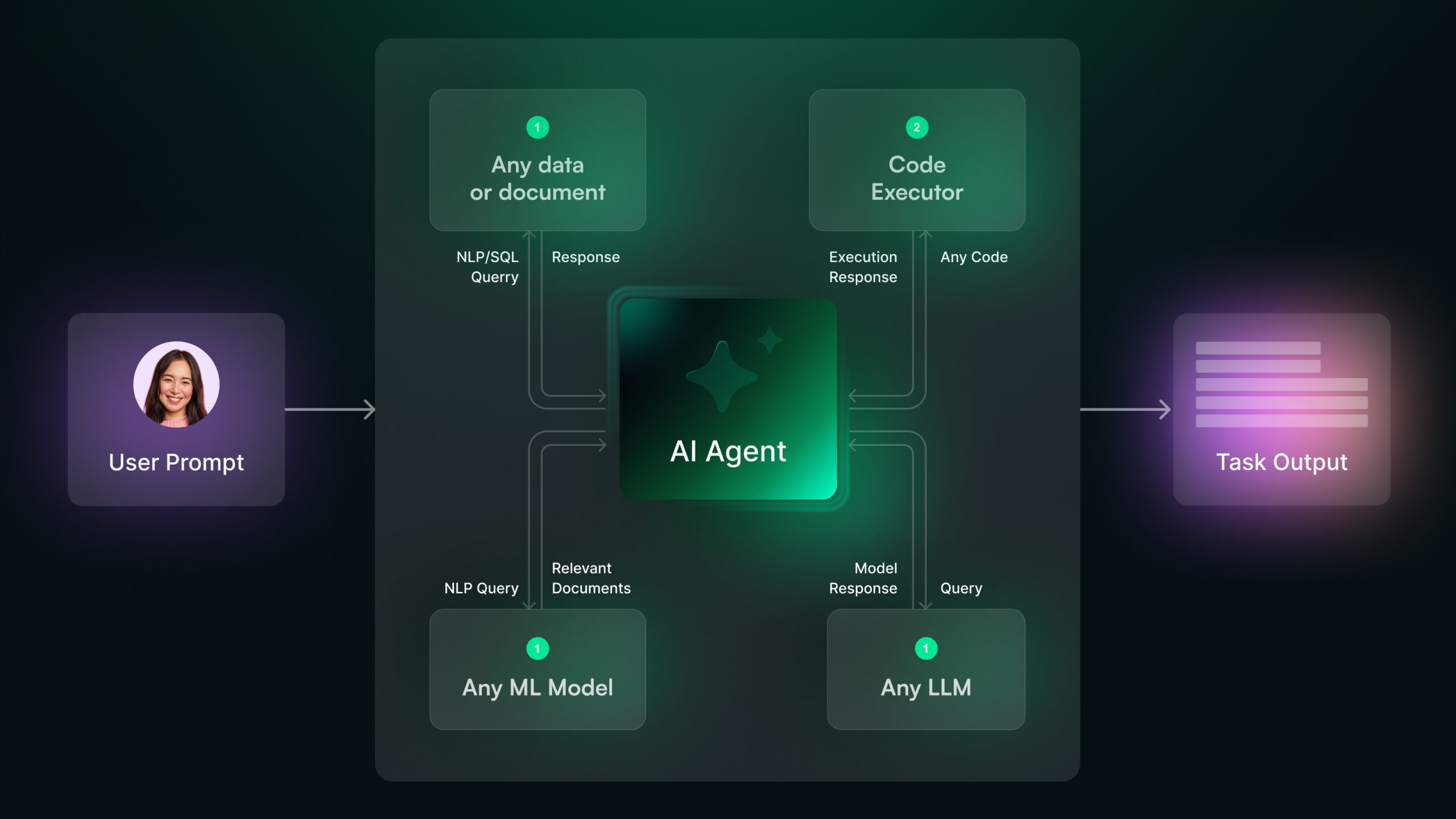
Agentic AI operates as an independent system capable of setting goals, making decisions, and taking actions without requiring constant human input. Its primary function is task execution, meaning it doesn’t just generate insights—it follows through by acting on them.
For example, an AI research assistant agent like Chatsonic can autonomously search for relevant information, summarize key findings, and draft reports without step-by-step human intervention.
Similarly, AI-powered supply chain management agents can predict inventory shortages, reorder stock, and optimize logistics in real-time.
Generative AI: Function as content creators:
Generative AI, on the other hand, is focused on creation rather than execution. It generates text, images, videos, music, or even code based on user input. Its primary function is content production, not decision-making or task execution.
For instance, AI chatbots like ChatGPT generate articles, summarize documents, or provide conversational responses, while DALL·E creates images from text descriptions.
However, these systems do not independently determine why something should be created or how it fits into a broader workflow. They need human guidance.
💡 Key difference: Agentic AI is action-oriented, while generative AI is output-driven.
2. Learning mechanisms and adaptability
Agentic AI: continuous learning and adaptation
AI agents rely on reinforcement learning and memory systems to improve over time. It learns from past experiences, refines decision-making strategies, and adjusts its actions based on real-world feedback.
For example, a financial AI agent analyzing stock market trends doesn’t just generate predictions.
The algorithm learns from past performance, adjusts its strategies, and modifies investment recommendations based on changing market conditions.
Generative AI: Predictive pattern recognition
Gen AI systems learn by recognizing and replicating patterns from massive datasets.
Models like GPT-4 or Stable Diffusion are trained on billions of data points to generate content miming human language, art, or music.
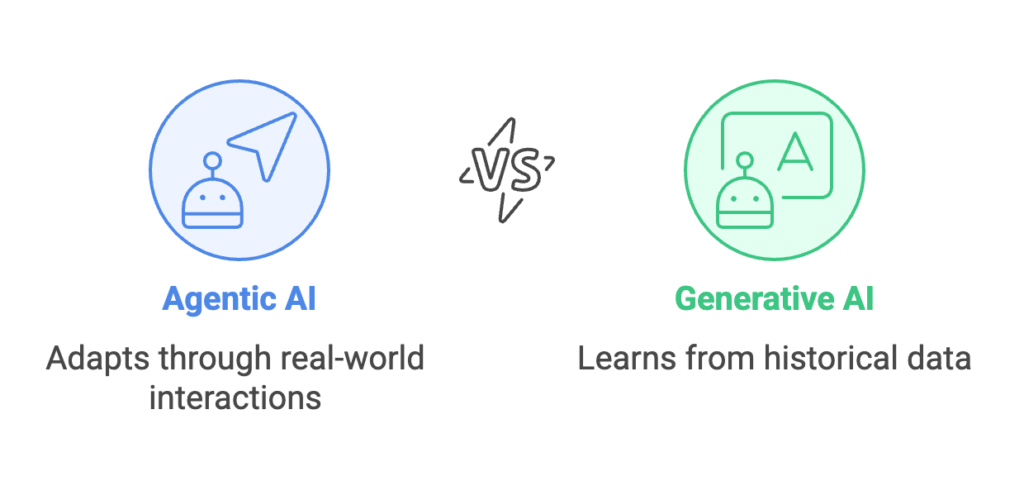
💡 Key difference: Agentic AI learns from real-world interactions and adapts; generative AI learns from historical data and predicts.
3. Decision-making processes
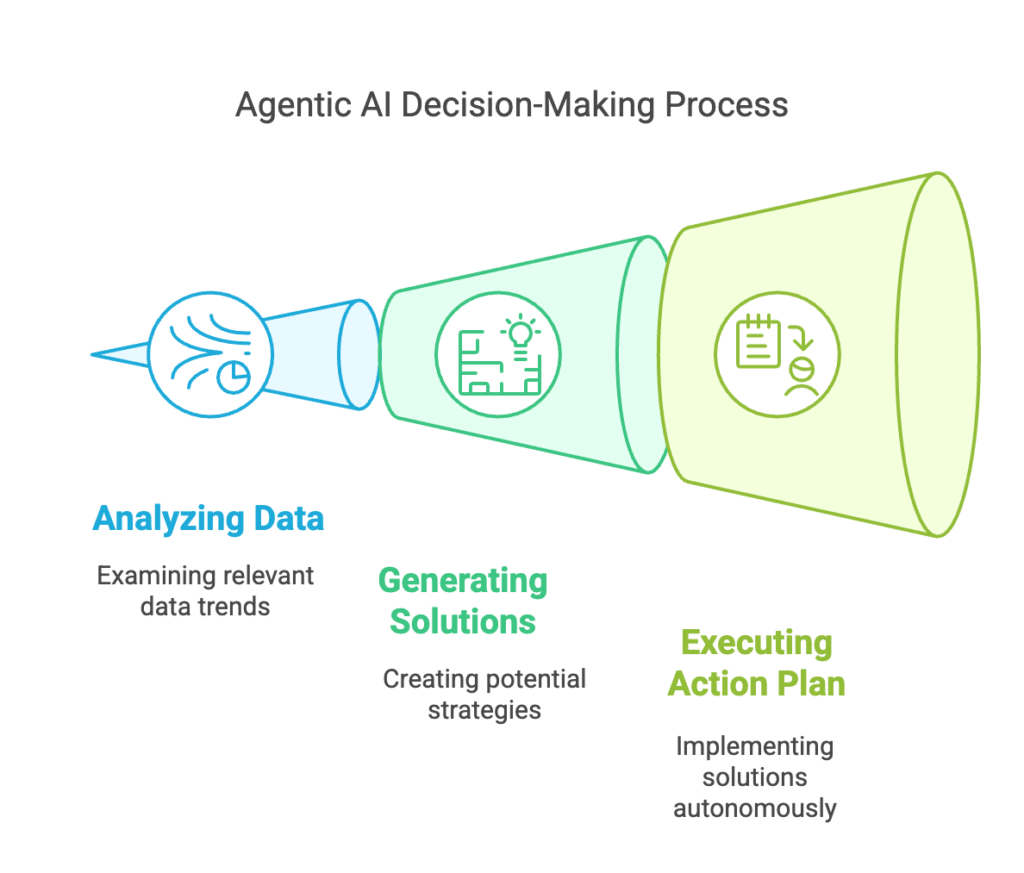
Agentic AI: Goal-oriented and autonomous
AI agent systems follow a structured decision-making process where it:
- Identifies a goal (e.g., improving customer engagement).
- Analyzes available data (e.g., browsing customer behavior trends).
- Generates possible solutions (e.g., launching personalized email campaigns).
- Executes an action plan without human intervention.
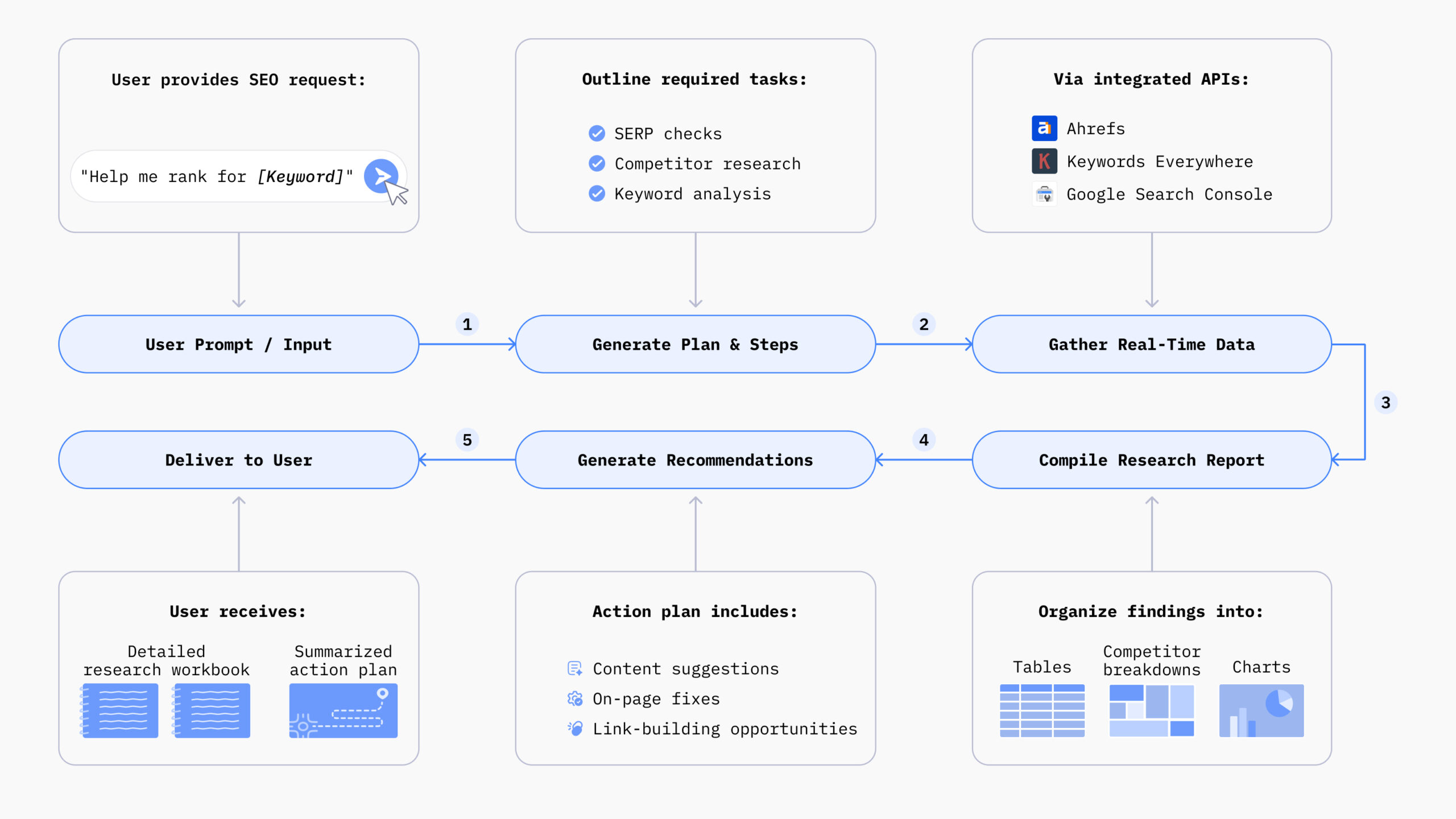
A great example is AI-powered SEO automation–where AI SEO agents can independently conduct keyword research, competitor analysis, analyze key metrics, and conduct audits without requiring manual input.
Generative AI: Follows prompts, no autonomous thinking
Generative AI does not make independent decisions. It responds to prompts by predicting the best possible answer based on its training data. It does not assess broader objectives or execute complex multi-step plans.
For instance, ChatGPT can suggest email subject lines based on a brand’s tone, but it won’t decide when to send them, analyze open rates, or adjust future emails based on performance—those steps require agentic AI.
💡 Key difference: Agentic AI thinks and acts, while generative AI responds and generates.
4. System integration capabilities
Agentic AI: Multi-system integration
Agentic AI is designed to integrate with multiple tools and software to automate workflows. It can connect with CRM systems, databases, analytics platforms, and APIs to make data-driven decisions and execute tasks.
For example, a customer support AI agent can pull customer purchase history from a CRM, analyze sentiment from support tickets, and resolve complaints—all in one workflow.
Generative AI: Standalone or API-based
Gen AI typically operates as a standalone model or as an API that businesses can plug into existing systems. While it can enhance automation by generating content, it does not inherently interact with external systems unless combined with agentic AI.
For instance, a legal AI assistant using generative AI can draft contracts but would require agentic AI to review legal compliance, gather relevant case law, and file the document.
💡 Key difference: Agentic AI integrates with systems for automation, while generative AI is often used as a standalone tool.
💡 Also read: 40 AI Agent Use Cases Across Industries [+Real World Examples]
5. Operational modes: Proactive vs. reactive
Agentic AI: Proactive and self-sufficient
Agentic AI operates proactively, meaning it anticipates needs, plans tasks, and executes them independently. It continuously assesses data, adjusts strategies, and takes corrective actions when necessary.
For example, AI cybersecurity agents detect anomalies in network traffic and take immediate action to prevent cyber threats—without waiting for human intervention.
Generative AI: Reactive and prompt-driven
Unlike agentic AI, generative AI is reactive, meaning it only works when prompted. It does not anticipate problems or initiate actions independently.
For example, an AI content writing tool will generate an article when asked but won’t autonomously decide when to publish it on WordPress.
💡 Key difference: Agentic AI initiates tasks; generative AI waits for instructions.
Agentic AI and gen AI in action: Example use cases
Agentic AI and generative AI serve distinct purposes but are often used together to create intelligent, automated systems.
Here’s how each type of AI is applied across industries:
Use cases of agentic AI (Task execution and automation)
- AI personal assistants: Unlike traditional AI chatbots, agentic AI assistants can go beyond answering questions. They schedule meetings, draft emails, analyze financial data, and even manage entire projects without human intervention.
- Business operations and automation: AI-driven supply chain agents can predict inventory shortages, reorder stock, and optimize logistics. AI-powered trading bots analyze market trends and execute trades in finance in real-time.
- Cybersecurity and threat detection: Security AI agents continuously monitor networks, detect anomalies, and take immediate action against cyber threats. Unlike traditional security software that simply flags risks, these AI agents respond automatically by blocking suspicious activity or updating security settings.
- AI for developers: Software development teams use agentic AI to debug code, run automated tests, and push updates to production. Instead of merely suggesting code (like GitHub Copilot), an AI coding agent can analyze performance issues and implement fixes autonomously.
Use cases of generative AI (Content creation and assistance)
- Content generation: Generative AI tools like Writesonic create blog posts, ad copy, email campaigns, and social media content at scale.
- Media and design: AI-generated visuals, videos, and animations are becoming common in advertising, gaming, and filmmaking. Creative professionals use tools like DALL·E and Runway ML to quickly generate custom graphics and video effects.
- Conversational AI and chatbots: Businesses integrate generative AI into customer support chatbots, like Botsonic, to automate communication while maintaining a humanized tonality.
- AI-powered research and reports: Professionals in law, finance, and academia use generative AI to summarize complex documents, draft legal contracts, and generate detailed research reports from large datasets.
- AI-assisted coding: Developers use generative AI tools to suggest code snippets, improve documentation, and generate boilerplate code for new projects.
Bottom line: Agentic AI excels at decision-making and task execution, while generative AI is best for content creation and creative problem-solving.
Combined, they unlock powerful automation solutions beyond simple responses or static content.
As AI continues to evolve, businesses and developers will increasingly rely on hybrid AI systems that can both generate and act, making workflows smarter and more efficient.
💡 Also check out: How AI Agents Work, Key Concepts and Mechanisms
Chatsonic: A powerful AI agent combining generative and agentic AI
One of the best examples of agentic AI in action is Chatsonic, an advanced AI-powered assistant developed by Writesonic.
Unlike basic generative AI tools that only generate text, Chatsonic combines generative and agentic AI capabilities to create content and analyze data, automate research-based tasks, integrate with other tools, and even browse the web for real-time information.
This makes Chatsonic more than just a content generator—it acts as an all-in-one AI-powered assistant that can think, create, and take action.
Here’s what makes this AI agent unique:
- Advanced content generation: Writes high-quality blog posts, ad copy, email sequences, and even technical documentation with customizable writing styles.
- Real-time web browsing: Unlike standard AI models that rely on static training data, Chatsonic pulls live, up-to-date information from the web, making it ideal for news, market trends, and research-based content.
- Workflow automation and system integration: Connects with key marketing tools, like Ahrefs and Google Search Console, for research and report generation. Also integrates with WordPress for direct content publishing.
For example, if you run a business, Chatsonic can help generate marketing assets for a campaign, analyze its success, create custom reports, and then suggest action items for future campaigns based on performance data—something traditional generative AI alone cannot do.
The future of AI isn’t just about content creation or automation—it’s about AI systems that think, act, and create.
And Chatsonic is one of the leading AI agents bridging the gap between generative AI (content) and agentic AI (execution), making AI smarter and more useful in real-world applications.
Try Chatsonic today and see how it transforms your workflows!
FAQs
1. What is the difference between generative AI and traditional AI?
Traditional AI follows strict rules to analyze data, make decisions, and automate tasks. Think of it like a smart assistant that helps sort, predict, or process information but only within clear boundaries.
Generative AI, on the other hand, is more creative. Instead of just following rules, it learns patterns from data and creates new content—whether that’s text, images, or even music. While traditional AI can help you organize photos, generative AI can generate completely new images based on a description.
The way they learn is also different. Traditional AI needs manual updates, like a software upgrade. Generative AI keeps learning and improving over time, much like how a person gains experience and skills.
2. How is agentic AI different from traditional AI?
Traditional AI can handle specific jobs but needs clear instructions. Agentic AI can understand goals and procedures, make decisions independently, and adapt to new situations.
Traditional AI works best in structured environments, like processing loan applications or analyzing medical scans. Agentic AI thrives in unpredictable situations, like managing logistics or offering personalized customer service, where it needs to understand the context and make smart choices.
3. Can agentic AI and generative AI work together?
While agentic AI and generative AI have distinct purposes, they can complement each other in various applications. Agentic AI can use generative AI’s outputs to make decisions and take actions, while generative AI can create content based on agentic AI’s insights and goals.



































![How to Scale Your Business Using B2B AI Agents [+ Tools to Try]](/wp-content/uploads/B2B-AI-Agents-scaled.jpg)



![40 AI Agent Use Cases Across Industries [+Real World Examples]](/wp-content/uploads/AI-Agent-Use-Cases-1-scaled.jpg)