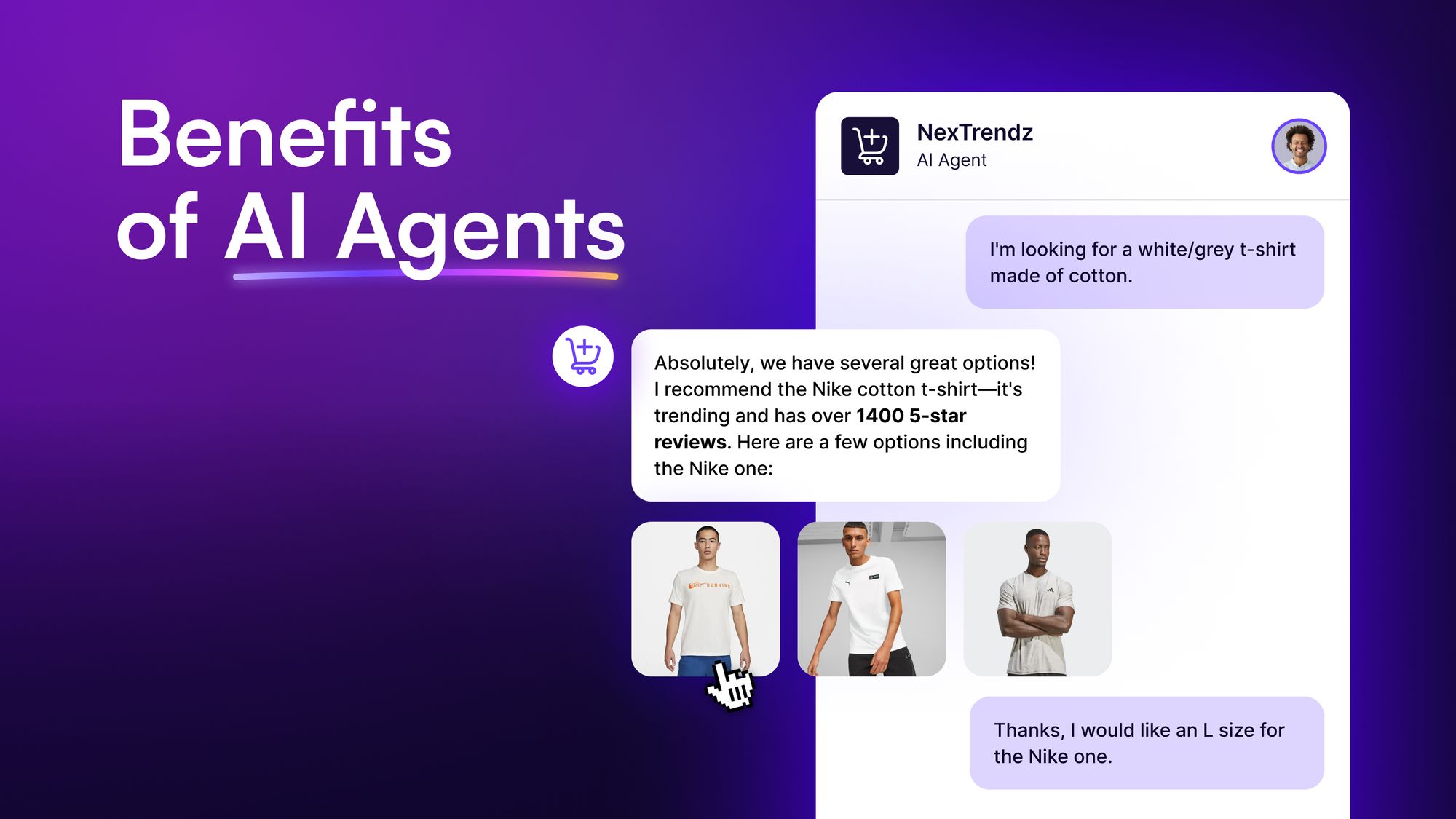
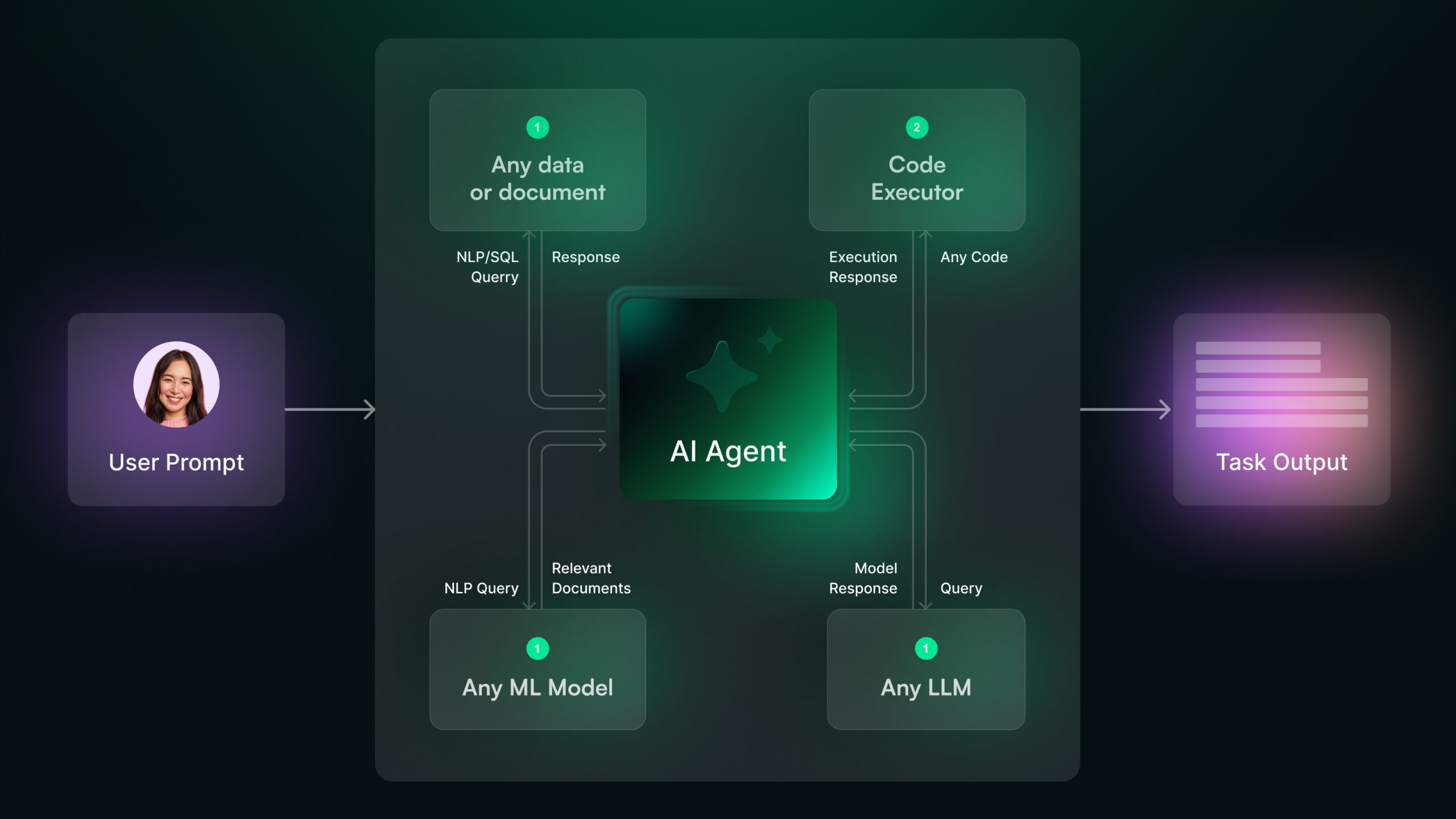
“AI Agents vs Agentic AI.” At first glance, these terms might look similar. In fact, many times the words are used interchangeably, but wrongly so.
While AI agents and agentic AI are both artificial intelligence systems that are changing how businesses handle their workflows, they are quite different in their purpose and functions.
In this article, we’ll compare AI agents vs. agentic AI in depth and understand their key features, problem solving capabilities, and cost implications for your business.
Let’s dive in.
AI Agents vs Agentic AI: A Quick Comparison
Here’s a quick comparison of agentic AI vs. AI agents before we get started with the in-depth article:
| Aspect | Agentic AI | AI Agents |
| Definition | Autonomous systems with goal-directed behavior | Specialized software for specific tasks within defined boundaries |
| Autonomy | High – operates without constant human oversight | Limited – follows predetermined protocols and rules |
| Decision-Making | Advanced reasoning, assesses multiple variables | Condition-action rules and specific algorithms |
| Learning & Adaptation | Continuous learning, applies knowledge across areas | Limited to specific areas, requires updates for new situations |
| Task Complexity | Handles complex tasks in unpredictable environments | Excels at specific, well-defined tasks in controlled settings |
| Core Components | Large Language Models, Integrated Tools, Memory Systems | Sensors, Perception System, Decision-making Module, Actuators |
| Resource Requirements | High – needs powerful computing and extensive data access | Lower – more economical for specific tasks |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Higher initial costs, better long-term value | Lower implementation costs, economical for specific tasks |
| Applications | Self-driving vehicles, personal assistants, industrial automation | Customer service, data processing, scheduling, marketing |
What is Agentic AI?
Agentic AI refers to systems that can operate autonomously and exhibit goal-directed behavior without constant human oversight. These systems possess the capability to perceive the environment, reason about complex situations, take independent action and learn from their experiences.
In contrast, traditional AI systems simply respond to specific inputs within predetermined parameters.
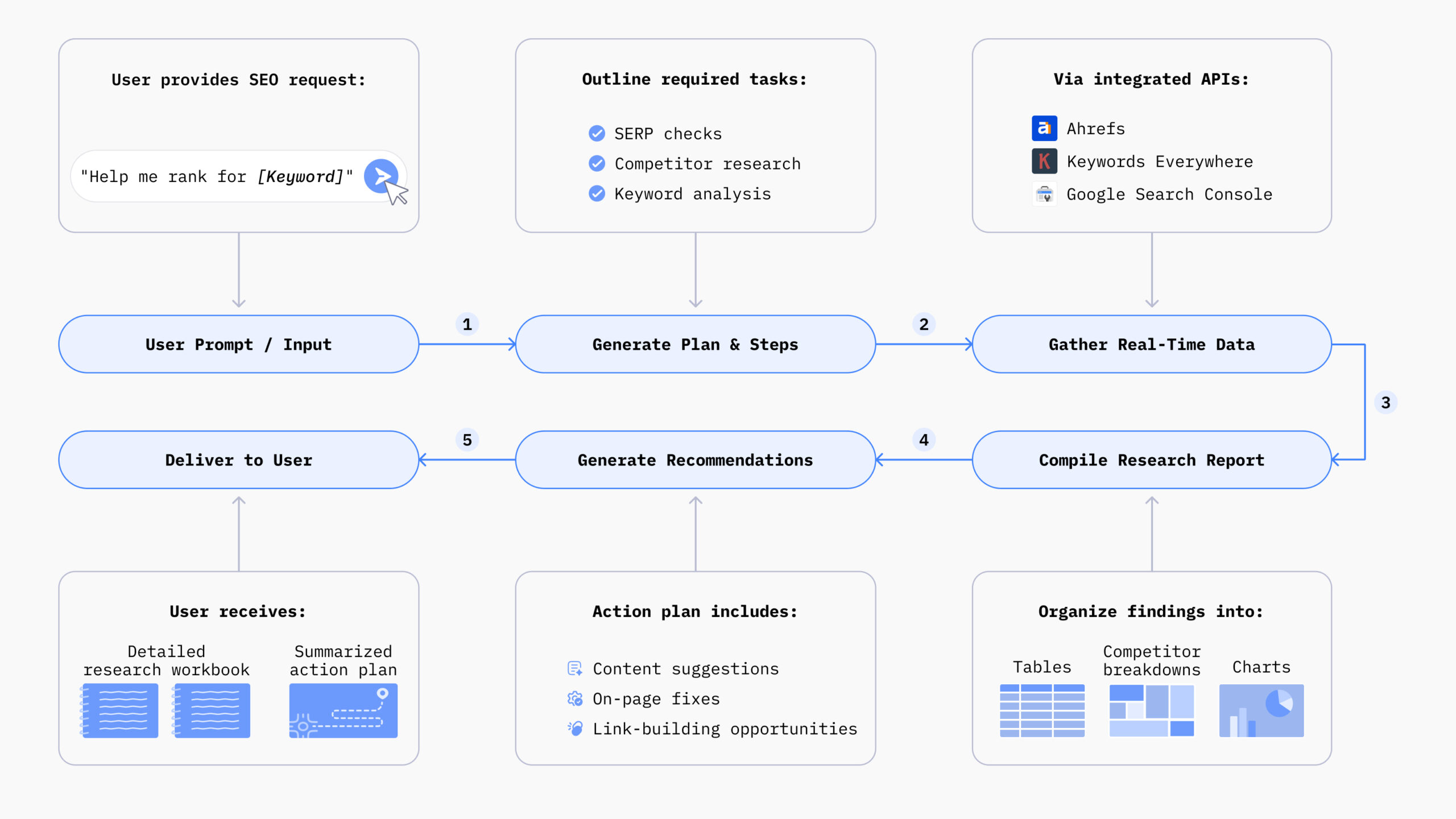
Agentic AI systems operate through four steps:
- Perception: Agentic AI can sense and interpret information from its environment using data inputs from sensors, cameras, or digital inputs to understand its surroundings.
- Decision-Making: It evaluates the information gathered, applies logic or learned patterns, and selects the most suitable course of action to achieve its objectives.
- Adaptability: Agentic AI learns from feedback and changing conditions, continuously improving its performance and refining its strategies over time.
- Autonomy: Once programmed with goals, it operates independently without the need for ongoing human guidance or intervention.
This autonomous capability allows them to adapt to changing circumstances and handle complex tasks that require sophisticated problem-solving abilities.
What makes agentic AI different is its proactive nature. Instead of waiting for explicit instructions, these systems can take initiative, anticipate future scenarios, and work toward defined objectives independently.
This makes them particularly valuable in applications ranging from self-driving vehicles to personal assistants and industrial automation, where autonomous decision-making and adaptive behavior are essential.
Core Components of Agentic AI
Three fundamental components work together in Agentic AI’s architecture.
- Large Language Models function as the cognitive engine that processes natural language and orchestrates complex behaviors.
- Integrated Tools give the system power to interact with external software, APIs, and databases. This extends its capabilities beyond simple text processing.
- Memory Systems provide both short-term retention for ongoing tasks and long-term storage of experiences and knowledge.
Key Features and Capabilities
One of the most important factors to focus on when comparing AI agents vs agentic AI are the key features. Agentic AI has slightly diverse capabilities compared to AI agents. They are capable of:
- Autonomous workflow design and execution
- Up-to-the-minute adaptation to changing environments
- Independent decision-making with minimal human oversight
- Integration with multiple data sources and tools
- Continuous learning from experiences and feedback
The system adapts to handle complex, multistep AI applications which cannot be done through traditional AI tools. That’s why, they now find applications in industries with complex workflows and critical decision-making requirements, such as healthcare and finance.
What are AI Agents?
AI agents are specialized software entities designed to perform specific tasks or functions within defined boundaries. Unlike the broader concept of agentic AI, these agents are purpose-built components that operate as part of larger systems, following predetermined protocols and rules.
They can be thought of as digital workers with specific job descriptions — each agent has clear responsibilities, methods of operation, and success criteria.
AI agents typically operate through a similar framework as AI agents. This includes sensing their environment, processing information according to programmed rules, and executing actions within their domain.
However, while they can exhibit autonomous behavior, their autonomy is limited to their designated functions. For example, a customer service AI agent might independently handle customer queries, but only within a predefined set of responses and scenarios. If there are queries outside their database, they may redirect it to a human agent.
These agents excel in task-specific applications where clear boundaries and predictable behavior are crucial. Some common areas where AI agents are used include:
- Automated customer service management
- Data processing tools
- Scheduling assistants
- Marketing agents and so on
Read our guide on what is an AI agent to learn about their functions, capabilities, and use cases.
Basic Structure of AI Agents
AI agents are built upon a fundamental architecture that enables them to interact with their environment and accomplish designated tasks.
The core structure consists of four key components:
- Sensors which gather information from the environment
- Perception system that processes and interprets this input
- Decision-making module that determines appropriate actions based on the agent’s programming and goals
- Actuators that execute these decisions.
This framework also contains a knowledge base that explains rules, procedures and learned patterns. This helps the AI agent to reference past experiences and established protocols.
The entire structure operates within a feedback loop, where outcomes of actions influence future decision-making processes.
Learn more about the structure and functions of AI agents with our guide “How do AI Agents Work?“
Common Applications of AI Agents
AI agents show remarkable versatility in different sectors:
- Healthcare systems use these agents to analyze patient data and provide live monitoring of vital signs.
- Manufacturing teams utilize them to optimize production processes and manage inventory levels with unmatched precision.
- Financial institutions use AI agents for fraud detection and automated trading systems. These agents monitor transactions and market conditions continuously and make split-second decisions based on complex algorithms.
- Customer service teams rely on AI agents to handle tasks from answering questions to processing returns. These systems work 24/7 to review customer feedback and manage support tickets accurately.
- Marketing teams use AI agents to conduct competitor research, create content, and analyze their marketing strategies for better outcomes.
AI Agents vs Agentic AI: Key Differences in Capabilities
When we compare AI agents vs agentic AI, there are clear differences in how they approach problem-solving and decision-making processes:
Decision-Making Processes
While both AI agents and agentic AI are capable of decision making, they process the queries differently.
Agentic AI uses advanced reasoning capabilities to assess multiple variables and predict outcomes before acting. It doesn’t just follow set rules but develops and adjusts strategies as circumstances change.
AI Agents only work within set boundaries and make decisions using condition-action rules and specific algorithms.
Learning and Adaptation
Agentic AI learns much like humans do, showing remarkable adaptability through ongoing learning. It processes new information and changes its behavior, which creates a feedback loop to boost performance over time.
These systems can also apply knowledge across different areas and scenarios.
AI Agents, on the other hand, mostly learn within their specific areas and need special programming or updates to handle new situations.
Task Complexity Handling
Both systems are designed to handle tasks of varying degrees of complexity.
Agentic AI can handle tasks even in unpredictable and changing environments. It breaks down complex goals into smaller, manageable tasks. However, AI Agents excel at specific, well-defined tasks in controlled settings, despite their limits.
This difference shows up clearly in financial trading. Agentic AI analyzes market trends and adapts strategies instantly, while AI Agents follow preset trading rules.
Resource Requirements
Each technology needs different levels of computing resources and infrastructure.
Agentic AI systems need powerful computing and reliable infrastructure to support their advanced reasoning and learning. They also need extensive data access and integration to work well due to their wide range of applications.
In comparison, AI Agents work with fewer resources, making them more economical for specific tasks.
Cost-Effectiveness
Agentic AI systems cost more to operate at first because they need sophisticated infrastructure and resilient computing resources.
AI agents offer a more economical solution for businesses with specific, well-laid-out tasks. Simple architecture and focused functionality keep their implementation costs lower.
Several factors determine the cost-effectiveness:
- Infrastructure Requirements: Agentic AI needs more sophisticated computing resources
- Maintenance Costs: AI agents need less ongoing maintenance
- Scalability Expenses: Agentic AI provides better long-term value despite higher upfront costs
- Training and Updates: AI agents require frequent updates for new scenarios
Conclusion
AI agents and agentic AI are two different artificial intelligence technologies — both having decision making and problem solving capabilities.
While AI agents excel at specific, predefined tasks, agentic AI offers greater autonomy and adaptability. If you want to choose between AI agents vs. agentic AI, you need to consider your business needs, resources, and desired outcomes.
If you’re looking to use AI for a specific use case such as marketing, it’s best to choose an AI agent like Chatsonic that’s built for the application. As they’ll be trained to deal with queries and provide high-quality outcomes for the use case, you’ll always get results that are similar or better than what you would with a human agent.
Ready to implement AI agents in your business? Try Chatsonic today!





































![How to Scale Your Business Using B2B AI Agents [+ Tools to Try]](/wp-content/uploads/B2B-AI-Agents-scaled.jpg)



![40 AI Agent Use Cases Across Industries [+Real World Examples]](/wp-content/uploads/AI-Agent-Use-Cases-1-scaled.jpg)