Imagine asking an AI model for a simple fact, only to receive a plausible-sounding but entirely fabricated response.
As surprising as this might sound for some, AI hallucination is something that is very real and often problematic.
This isn’t just a minor hiccup. It can have serious consequences in fields like healthcare, finance, research, and even journalism.
But why does this happen, and more importantly, how can we prevent it?
In this blog, we’ll explain what is AI hallucination, why this phenomena occurs, and explore actionable strategies for tackling it.
What you’ll learn from this blog:
- The definition and examples of AI hallucinations in simple terms.
- The underlying reasons why AI models hallucinate and generate errors.
- The risks posed by hallucinations across industries.
- How to avoid AI hallucination when using large language models.
- How Writesonic can help you generate reliable and human-like AI content.
What are AI hallucinations?
An AI hallucination occurs when an AI model generates incorrect or misleading information that appears plausible.
Think of it as an AI “making things up” without any basis in reality.
AI hallucinations are most common in natural language processing (NLP) chatbots like OpenAI’s ChatGPT or Google’s Bard. These models are trained to predict and generate text based on vast datasets.
So when the data is incomplete, biased, or irrelevant to the prompt, the model may fabricate information to “fill the gaps.”
This output may look convincing, but it can be dangerously inaccurate.
Recent analysis reveals that chatbots hallucinate approximately 27% of the time, and factual errors show up in 46% of their generated texts).
This means almost half of all AI-generated content has some type of inaccuracy!
Example:
If you ask AI, “Who invented gravity?” you might get an answer like, “Isaac Newton in 1602.”
While Newton did study gravity, the year and details might be fictional. The AI isn’t lying—it simply doesn’t know the right answer and tries to generate one based on its training.
But why the name “hallucination”?
The term “hallucination” draws a parallel to human behavior.
Just as people can perceive things that aren’t there, AI models can generate information without grounding it in reality.
But unlike humans, AI lacks intent—it isn’t trying to deceive but simply lacks the capability to verify its own output.
Key characteristics of AI hallucinations:
- Seemingly confident tone: AI often presents fabricated data with a convincing and authoritative tone.
- Contextually plausible but factually incorrect: The response fits the question but doesn’t hold up under scrutiny.
- Hard to detect: For non-experts, spotting hallucinations can be challenging, as the errors are subtle.
AI hallucinations highlight a critical flaw in even the most advanced models: their inability to distinguish fact from fiction.
As we delve deeper, you’ll see how this issue stems from their very design—and how to work around it effectively.
Types of AI hallucinations with examples
AI hallucinations manifest in several ways, depending on how the model processes inputs and generates outputs.
Let’s break down the most common types, each with examples to help you understand their impact.
1. Factual inaccuracies: Generating incorrect data
Factual inaccuracies occur when AI provides information that seems believable but is fundamentally wrong.
These errors often arise because the model generates content based on patterns in its training data rather than validated facts.
Example:
Google’s Bard chatbot once announced that the James Webb Space Telescope took the first-ever photo of an exoplanet.
The claim sounded great, except the first exoplanet images came from 2004, long before Webb existed!
This type of hallucination is particularly problematic in critical applications like healthcare, where even a minor error can lead to serious consequences.
Now, just imagine if AI chatbots were to provide incorrect drug dosage instructions. It could be life-threatening, to say the least!
2. Contextual misunderstandings: Misinterpreting intent or context
Sometimes, AI misunderstands the nuances of a question or the specific context, leading to responses that are irrelevant or nonsensical.
This often happens when prompts are ambiguous or too broad.
AI can often struggle with:
- Industry-specific contexts
- Cultural nuances
- Historical context
- Emotional undertones
Example:
For instance, when Microsoft’s Bing AI analyzed earnings statements from Gap and Lululemon, it produced a perfectly confident but completely incorrect summary of their financial figures.
The AI understood the format but missed crucial contextual details about financial reporting.
These misunderstandings highlight the importance of clear and precise prompts when interacting with AI models.
3. Creative overreach: Unprompted elaborations by AI models
Here’s where things get interesting.
Sometimes AI doesn’t just get facts wrong–it gets creative in ways you never asked for.
Creative overreach occurs when AI “makes up” information to complete a response, even if the input didn’t request it.
While this can be useful in creative writing or brainstorming, it’s a red flag in factual or professional contexts.
Example:
We asked ChatGPT about a nonexistent term, “cycloidal inverted electromagnon.”
But the AI didn’t admit ignorance.
Instead, it created an elaborate explanation that seemed so convincing that we had to double-check if “cycloidal inverted electromagnon” is actually a real phenomenon!
What makes these creative hallucinations particularly tricky is how AI can “double-down” on its mistakes.
When questioned about potential errors, instead of admitting mistakes, AI systems sometimes generate even more elaborate but incorrect explanations.
Understanding these types of hallucinations is the first step toward mitigating their risks.
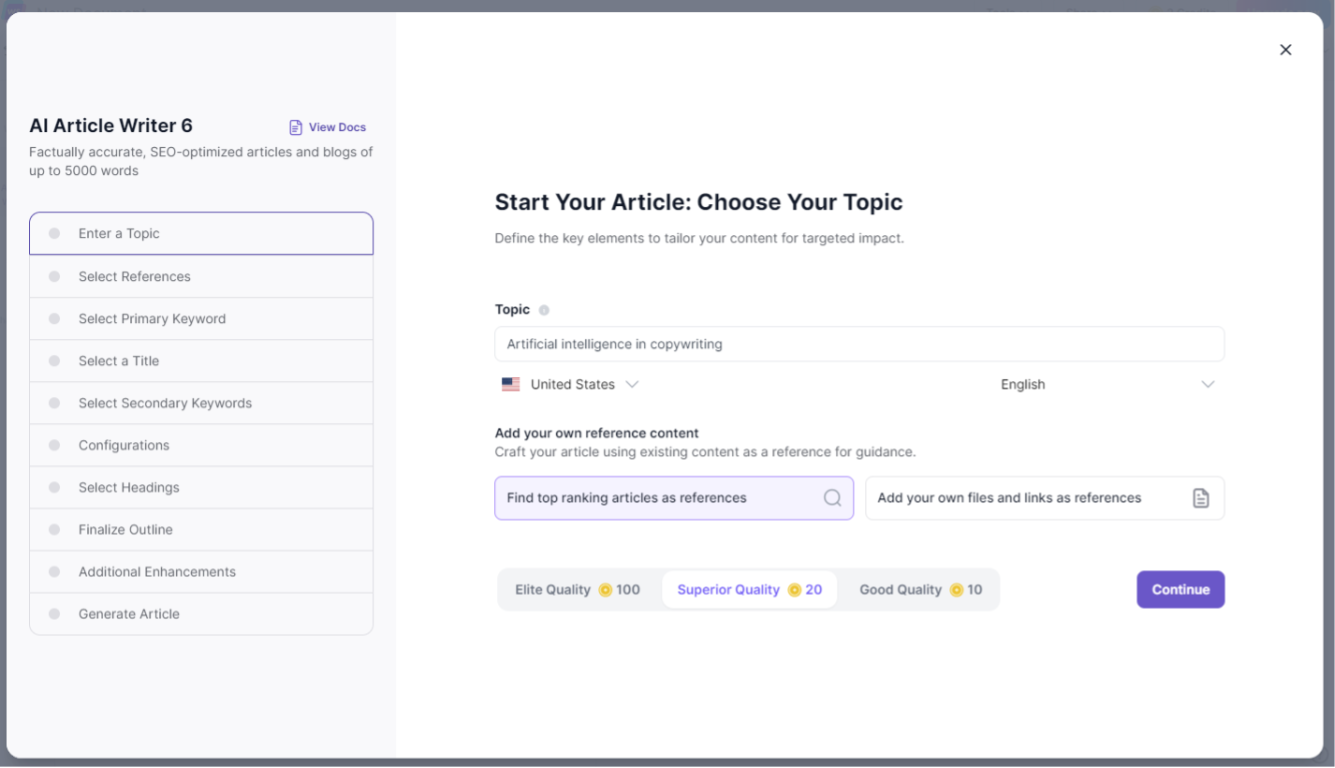
💡 Pro tip: Want an AI article generator that actually gets its facts right? Try Writesonic’s AI Article Writer.
It delivers real-time data on the latest topics, ensures every piece is fact-checked and cited, and uses in-depth web research for accuracy you can trust.
No made-up facts, just reliable, high-quality content in under 10 minutes.
Check it out—you might just find your next favorite AI content tool. 😉
How can AI hallucinations be avoided when using language models?
AI hallucinations—when AI generates inaccurate but convincing information—can be frustrating, but they’re manageable with the right approach.
Here are a few tried and tested approaches from the Writesonic team that can help you prevent AI hallucinations:
- Be specific with prompts: Clear, detailed instructions help AI deliver accurate and relevant results.
- Fact-check everything: Don’t rely solely on AI. Cross-check critical information with trusted, reliable sources.
- Involve humans where it matters: For high-stakes content, human oversight ensures accuracy and context that AI alone can’t guarantee.
- Keep things up to date: Review and refresh your processes regularly to align with the latest information and best practices.
- Adopt advanced techniques: Certain prompt engineering techniques are a great way to ground AI outputs.
To go more in-depth about these techniques, here’s a more detailed overview:
1. Learn how to prompt AI and LLMs effectively
The quality of AI-generated content is heavily influenced by the clarity and specificity of user prompts.
In short, your prompts work like a GPS for AI. The clearer your directions, the better your output will be.
While on the other hand, ambiguous or broad prompts can lead to AI generating inaccurate or fabricated information.
Strategies for effective prompting:
- Be specific and clear: Instead of asking, “Tell me about AI,” specify, “Explain the causes of AI hallucinations in large language models”
- Set explicit instructions: Direct the AI on the desired format or depth, such as, “Provide a concise summary of the latest research on AI hallucinations in 200 words for a beginner..”
- Use structured prompts: Incorporate bullet points or numbered lists to guide the AI in organizing information systematically.
Example:
Instead of saying, “Describe renewable energy,” you can make your prompt for AI more detailed like this:
“Write a 200-word explanation about renewable energy adoption trends in 2023.
The audience is small business owners exploring green initiatives.
Use data from credible sources like the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) or World Bank to highlight three specific benefits.”
This level of detail ensures the AI understands the purpose, audience, and sources to use, minimizing the risk of hallucinations and delivering more accurate results.
To make AI even more specific, direct your prompt with examples and reference documents or links.
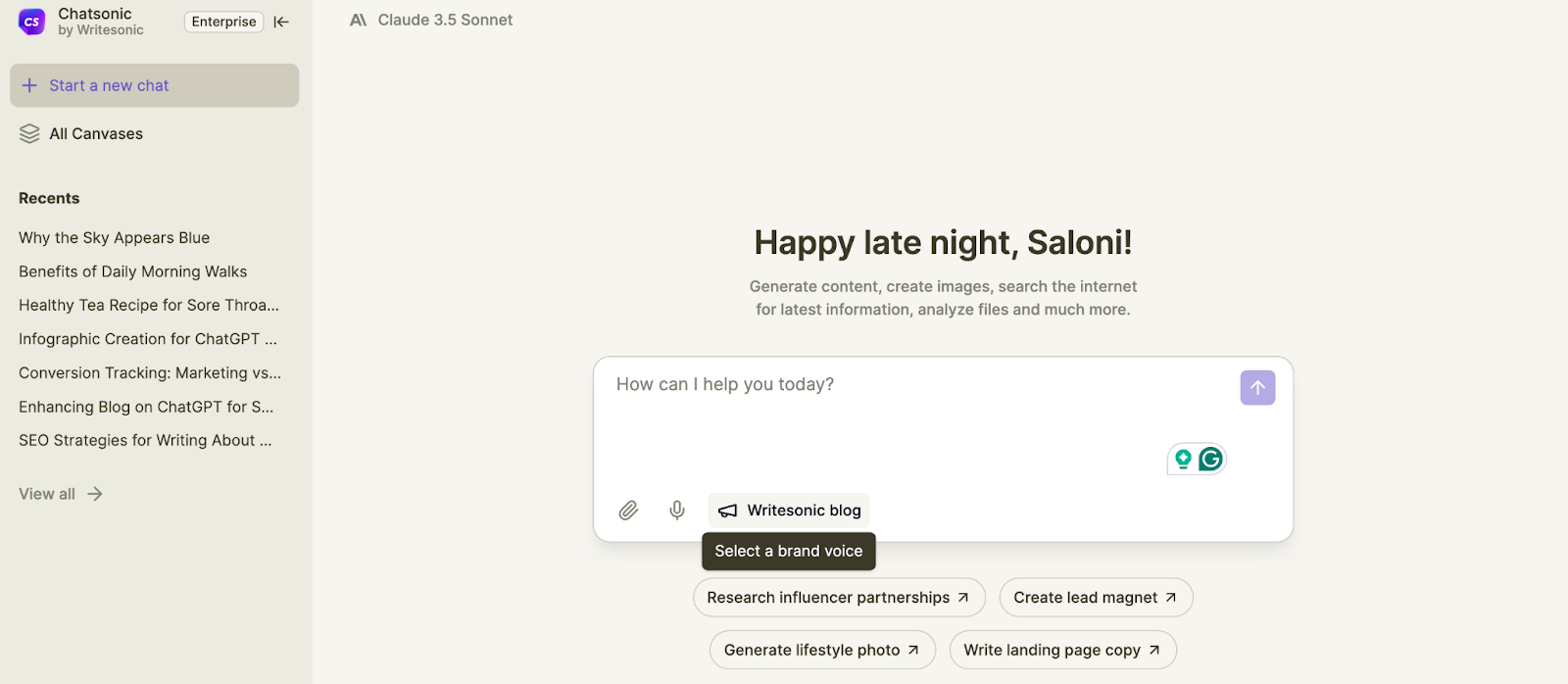
And here’s the good news—tools like Chatsonic make this so much more easier.
With features like data ingestion and deep web research, Chatsonic delivers ensures accurate and fact-checked results.
Need specific insights? You can upload PDFs, CRMs, or even PowerPoints and let the AI extract reliable information.
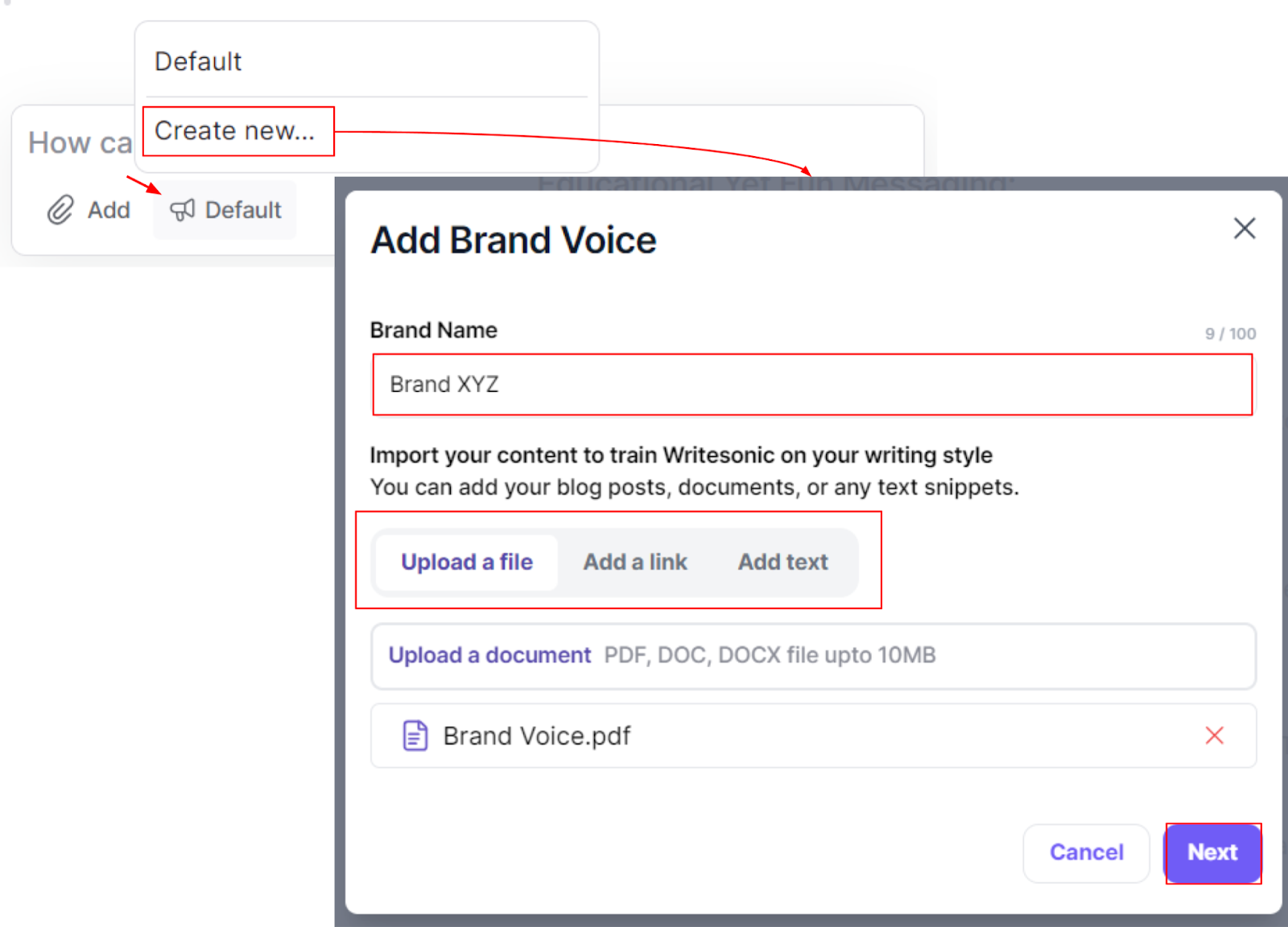
Plus, you can customize the brand voice to match your unique tone, so everything feels like you.
And if you’re crafting articles, Writesonic also allows you to input brand voice configurations and custom guidelines, combined with factual accuracy with real-time research.
2. Experiment with temperature
One of the most overlooked yet powerful tools for reducing AI hallucinations is adjusting the temperature setting.
In AI language models, temperature controls the randomness of the outputs—essentially, how “creative” or “safe” the AI will be when generating responses.
Here’s how temperature settings work:
- Lower temperature values (e.g., 0.2) make the AI more deterministic, leading to precise and repetitive outputs. This is ideal for tasks requiring factual accuracy, like summarizing research or generating how-to guides.
- Higher temperature values (e.g., 0.8 or above) introduce more randomness and creativity, often at the expense of accuracy. This can be useful for brainstorming ideas or creative writing but is more prone to hallucinations.
For example:
Let’s say you’re using an AI tool to generate a story introduction about an astronaut landing on a mysterious planet.
With a high temperature setting (e.g., 0.9), the AI might produce something highly imaginative but overly dramatic or nonsensica like:
“The planet shimmered with glowing rivers of molten gold, and the trees whispered ancient secrets in a language no human could understand.
But suddenly, the ground dissolved beneath the astronaut’s feet, plunging them into a world of infinite mirrors.”
On the other hand, by lowering the temperature (e.g., 0.3), the AI generates a more grounded and coherent introduction:
“The astronaut stepped onto the surface of the red-tinged planet, their boots kicking up fine dust.
In the distance, jagged mountains stretched toward the sky, and a faint hum echoed through the air, hinting at something extraordinary waiting to be discovered.”
💡Pro tip: When accuracy matters, start with a lower temperature (0.2-0.3) and gradually increase it if the outputs feel too rigid or lack depth. For creative tasks where accuracy is less critical, a higher temperature (0.7-0.8) can be more effective.
3. Leverage prompt engineering techniques
Prompt engineering is about more than just asking the AI a question.
It’s a deliberate strategy to guide the AI’s behavior, improve accuracy, and minimize hallucinations.
Here are some prompt engineering methods for optimizing your use of AI chatbots:
A. Match the tool to the task
Not all AI models are designed for every purpose.
Using a general-purpose AI for highly specific or niche tasks can lead to hallucinations because the model isn’t equipped for that level of expertise.
For example, a tool like ChatGPT, built for conversational tasks, may struggle with legal citations or scientific accuracy.
What you can do:
Choose an AI tool designed for the specific task at hand. For instance:
- Use tools like Writesonic solely for content creation.
- Leverage tools specialized for technical or scientific tasks, such as research assistants trained on domain-specific data.
💡Pro tip: When it comes to marketing-related tasks, Chatsonic is a perfect fit.
It pulls real-time data from tools like Ahrefs, Hubspot, and Google Search Console, giving you everything you need for SEO, ads, and campaign planning—all in one place.
Say goodbye to switching tabs and hello to streamlined, data-driven strategies.
B. Use role-based instructions
You can improve the AI’s performance by assigning it a specific role in the prompt. This technique helps narrow the AI’s focus and ensures outputs that align with your needs.
Example prompts:
- “You are an SEO expert. Write a blog intro explaining how to optimize for Google’s E-E-A-T guidelines.”
- “You are an experienced math tutor for high school students. Solve this problem step by step and explain each calculation.”
Role-based instructions frame the task in a way that reduces ambiguity, steering the AI toward more precise and useful outputs.
Also read: 10 Best AI Chatbots for 2024
C. Apply chain-of-thought or least-to-most prompting
Complex tasks often trip up AI models, leading to hallucinated outputs.
Using techniques like chain-of-thought or least-to-most prompting can help break down complex queries into manageable steps, improving accuracy and logic.
How it works:
- Chain-of-thought prompting encourages the AI to explain its reasoning step by step. For example:
“Explain how the United Nations was formed by listing the key events and their years in chronological order.” - Least-to-most prompting starts with simple tasks and builds complexity. For instance:
“First, identify the key themes in this article. Then, summarize each theme in 100 words.”
These methods not only enhance accuracy but also allow you to verify the AI’s reasoning at each stage.
For example, if you want AI to create an article for you, instead of simply asking it to create content based on the topic and additional guidelines, ask the model to provide the blog section by section.
D. Limit response formats
Providing specific instructions on how you want the AI to format its response can reduce errors and hallucinations.
Structured outputs leave less room for the AI to deviate from your expectations.
Examples of structured prompts:
- “List three benefits of renewable energy in bullet points with credible citations.”
- “Write a 150-word product description about Writesonic followed by a call-to-action. ONLY cover the tool’s SEO features, nothing else.”
- “Give me a table with the pros and cons of creating bulk content for marketing. Do not provide any information found on [specific URL].”
When the AI knows exactly what’s expected, it’s less likely to fabricate information or wander off-topic.
4. Establish human-in-the-loop systems
Human-in-the-loop (HITL) systems combine the efficiency of AI with the expertise of humans.
Think of it as a collaboration where humans step in to guide, correct, or enhance AI outputs.
They add human intuition to AI’s speed, ensuring outputs are accurate, ethical, and reliable.
A HITL system works in three simple steps:
- During training: Humans label and curate data to ensure the AI learns from accurate examples. This is like teaching a student the right answers before a test.
- Real-time corrections: When AI generates outputs, humans step in to review and fix errors. For example, in customer support, an agent can take over when a chatbot struggles with a complex query.
- Feedback loops: Every correction helps the AI improve. It learns from human edits and becomes better over time.
Where does a human-in-the-loop system shine?
- Healthcare: AI can analyze scans quickly, but doctors validate findings to avoid misdiagnoses.
- Content moderation: AI flags harmful posts, but human moderators decide what stays or goes.
- Legal drafting: AI drafts documents and lawyers review for compliance and accuracy.
- Fact-check AI-generated outputs thoroughly
When it comes to Your Money or Your Life (YMYL) topics like health, finance, or legal advice, inaccuracies can have serious consequences.
Google’s E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) guidelines hold publishers accountable for delivering accurate content—even when it’s AI-generated.
Here’s how to ensure thorough fact-checking:
- Verify with credible sources
Always cross-check AI-generated information with authoritative organizations.
For health topics, use trusted sources like the World Health Organization (WHO) or CDC. For finance, consult IRS.gov, World Bank reports, or other official databases
Example: If AI generates a claim like “Investing in AI startups guarantees 40% returns,” validate this against industry data or financial reports to ensure accuracy.
- Collaborate with experts
Involve subject matter experts for sensitive or complex topics. Their input can refine AI outputs and avoid risky misinformation. As a bonus, it will also help your content rank better as it will align with Google’s E-E-A-T guidelines.
Example: A licensed attorney reviewing AI-written legal content ensures compliance with local regulations, adding credibility to the final piece.
- Leverage verification tools
Tools like FactCheck.org, or Google Scholar are excellent for verifying claims. Remember to:
- Verify claims against reliable sources.
- Check cited references.
- Look for inconsistencies.
- Document verification processes.
- Keep content updated
YMYL topics evolve rapidly, so regular audits are essential to ensure your content reflects the latest information.
Outdated advice in healthcare or technology can mislead readers and damage trust.
Why do AI hallucinations happen?
AI hallucinations don’t appear out of thin air.
They result from specific challenges and limitations in how AI models are designed, trained, and deployed.
Let’s break down the major reasons why these errors in AI occur:
1. Insufficient or biased training data
AI models are only as good as the data they’re trained on. If the training data is incomplete, outdated, or biased, the AI will inevitably generate flawed or skewed responses.
Training datasets often lack diversity or accuracy, reflecting human biases or information gaps.
For instance, research shows that facial recognition systems trained primarily on one ethnic group showed significantly reduced accuracy when identifying individuals from other ethnicities.
This means if you prompt AI to generate a list of renowned female scientists, the model might overlook key figures from Asia or Africa simply because the data on these individuals wasn’t adequately represented during training.
2. Overfitting issues
Overfitting happens when an AI model “memorizes” its training data instead of learning general patterns.
While this might make the model perform well on specific tasks, it significantly reduces its ability to adapt to new inputs.
Overfitting makes AI overly reliant on the patterns it has seen before. As a result, AI models find patterns between input and output data without grasping the underlying logic.
3. Algorithmic limitations
AI models like GPT or BERT are designed to predict and generate the next most likely word based on statistical probabilities.
However, they don’t inherently “understand” context or verify the truthfulness of the outputs.
Instead, AI spots patterns between input and output data without learning the mechanisms. This basic limitation explains why AI systems often give confident but nonsensical answers.
| Limitation type | Impact on output |
| Pattern matching | Creates false correlations |
| Context understanding | Misses subtle nuances |
| Knowledge gaps | Generates fabricated details |
4. Prompt ambiguity
Your choice of words matters more than you might think. When you provide vague or unclear prompts, AI systems might misinterpret your intent.
Research indicates that prompt clarity significantly impacts response accuracy, with ambiguous prompts leading to increased hallucination rates.
For example, if you ask AI, “What are the key features of Mars?” without specifying whether you mean the planet or the chocolate bar, the model might produce a mixed response that includes scientific facts and nutritional values.
Also read: How To Write Better ChatGPT Prompts
5. Adversarial inputs
Questions phrased in certain ways can trick AI systems.
These “adversarial inputs” force misclassifications based on the model’s training patterns.
They work like loopholes in the AI’s logic, and bad actors can exploit these weaknesses to generate false information.
AI systems constantly balance between being too rigid (underfitting) and too specialized (overfitting).
Models trained on limited or biased datasets often repeat errors from their training data.
This explains why AI assistants might confidently mention fake sources or create believable but fictional content.
Why are AI hallucinations a problem?
The consequences of AI hallucinations aren’t just technical glitches.
They lead to real-world problems that can impact your business, reputation, and bottom line.
Here’s why you need to take these AI mishaps seriously:
1. Impact on user trust
When your AI system starts spinning tales, your users’ confidence takes a hit.
Studies show that AI hallucinations significantly diminish user trust and satisfaction levels.
Think about it–If you can’t rely on an AI writing tool to give you accurate information, why would you keep using it?
The trust issue becomes even more critical in sectors like healthcare and finance, where accuracy is not only a nice to have but an absolute essential.
When users discover that an AI system has been confidently presenting false information, they don’t just doubt that specific response.
They question everything the system has ever told them.
2. Potential for misinformation
The spread of misinformation through AI systems isn’t just a minor inconvenience–it’s a serious concern that can snowball quickly.
Here’s what makes it particularly dangerous:
- AI systems present false information with high confidence.
- Misinformation can spread rapidly across multiple channels.
- Users often struggle to distinguish AI-generated content from human-created information.
- The impact multiplies when one error leads to a chain of false information.
| Impact area | Consequence |
| Healthcare | Incorrect diagnoses and treatment suggestions |
| Finance | Flawed credit assessments and stock predictions |
| Supply Chain | Inventory issues affecting revenue |
| Research | Wasted resources on false leads |
3. Reputational damage for businesses
When AI systems hallucinate, your brand’s reputation is on the line.
Consider this recent instance:
When Google’s AI made a factual error in a demo, its stock price dropped 7.7%, resulting in a nearly $100 billion loss in market value.
That’s not just a temporary setback—it’s a stark reminder of how AI hallucinations can impact your bottom line.
The damage doesn’t stop there. When AI chatbots provide incorrect information to customers, it can lead to:
- Immediate loss of customer trust.
- Long-term brand reputation damage.
- Potential legal challenges and compliance issues.
- Financial losses from misinformed decisions.
- Decreased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
This is particularly challenging because AI hallucinations can affect between 27% and 46% of generated content.
That’s nearly half of all AI outputs potentially containing some form of inaccuracy.
In regulated industries, these errors aren’t just embarrassing. They can lead to serious compliance violations and legal challenges.
You might also like: 6 Best AI Prompt Marketplaces to Know in 2024
Wrapping up
AI is a powerful tool, but it needs direction. By fact-checking outputs and refining your approach, you can make AI a reliable ally in creating content you can trust. It’s about working smarter, not just faster.
Looking for the most accurate AI tool for content creation?
Let’s face it—fact-checking AI outputs and tweaking responses can feel like a full-time job.
But it doesn’t have to be. With tools like Writesonic and Chatsonic, creating reliable, high-quality content is simpler and smarter.
Writesonic’s AI Article Writer is like having a research assistant, and editor rolled into one. It doesn’t just churn out text—it delivers content you can trust.
- It pulls real-time data to ensure your articles are fresh and relevant, no matter the topic.
- Every output is fact-checked and cited, so you know exactly where the information comes from.
- It even adapts to your brand voice and style, keeping your messaging consistent.
Imagine crafting a 2,000-word blog post in minutes, complete with accurate statistics and polished language. With Writesonic, it’s not just possible—it’s effortless!
For more interactive content needs, Chatsonic steps in. It’s not your average chatbot; it’s designed to dive deeper into your queries and deliver precise, actionable answers.
- Need quick SEO insights? Chatsonic connects to live Google Search, pulling real-time updates.
- Have a specific report to summarize? Just upload your file, and Chatsonic will extract key insights in seconds.
- Want marketing magic? It integrates seamlessly with tools like Ahrefs and HubSpot, making campaign planning a breeze.
From long-form blogs to interactive brainstorming sessions, Writesonic ensures your outputs are accurate, relevant, and aligned with your goals.
No guesswork. No wasted effort.









![21 Practical Ways to Use AI [Examples + Tools]](/wp-content/uploads/How-to-use-AI-scaled.jpg)


![140 Best AI Tools: Rated & Reviewed [2025]](/wp-content/uploads/Best-AI-Marketing-Tools-1-1.jpg)